- 做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目) (opens new window)
- 刷算法(两个月高强度学算法) (opens new window)
- 背八股(40天挑战高频面试题) (opens new window)
# 583. 两个字符串的删除操作
给定两个单词 word1 和 word2,找到使得 word1 和 word2 相同所需的最小步数,每步可以删除任意一个字符串中的一个字符。
示例:
- 输入: "sea", "eat"
- 输出: 2
- 解释: 第一步将"sea"变为"ea",第二步将"eat"变为"ea"
# 算法公开课
《代码随想录》算法视频公开课 (opens new window):LeetCode:583.两个字符串的删除操 (opens new window),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解。
# 思路
# 动态规划一
本题和动态规划:115.不同的子序列 (opens new window)相比,其实就是两个字符串都可以删除了,情况虽说复杂一些,但整体思路是不变的。
这次是两个字符串可以相互删了,这种题目也知道用动态规划的思路来解,动规五部曲,分析如下:
- 确定dp数组(dp table)以及下标的含义
dp[i][j]:以i-1为结尾的字符串word1,和以j-1位结尾的字符串word2,想要达到相等,所需要删除元素的最少次数。
这里dp数组的定义有点点绕,大家要理清思路。
- 确定递推公式
- 当word1[i - 1] 与 word2[j - 1]相同的时候
- 当word1[i - 1] 与 word2[j - 1]不相同的时候
当word1[i - 1] 与 word2[j - 1]相同的时候,dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
当word1[i - 1] 与 word2[j - 1]不相同的时候,有三种情况:
情况一:删word1[i - 1],最少操作次数为dp[i - 1][j] + 1
情况二:删word2[j - 1],最少操作次数为dp[i][j - 1] + 1
情况三:同时删word1[i - 1]和word2[j - 1],操作的最少次数为dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 2
那最后当然是取最小值,所以当word1[i - 1] 与 word2[j - 1]不相同的时候,递推公式:dp[i][j] = min({dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 2, dp[i - 1][j] + 1, dp[i][j - 1] + 1});
因为 dp[i][j - 1] + 1 = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 2,所以递推公式可简化为:dp[i][j] = min(dp[i - 1][j] + 1, dp[i][j - 1] + 1);
这里可能不少录友有点迷糊,从字面上理解 就是 当 同时删word1[i - 1]和word2[j - 1],dp[i][j-1] 本来就不考虑 word2[j - 1]了,那么我在删 word1[i - 1],是不是就达到两个元素都删除的效果,即 dp[i][j-1] + 1。
- dp数组如何初始化
从递推公式中,可以看出来,dp[i][0] 和 dp[0][j]是一定要初始化的。
dp[i][0]:word2为空字符串,以i-1为结尾的字符串word1要删除多少个元素,才能和word2相同呢,很明显dp[i][0] = i。
dp[0][j]的话同理,所以代码如下:
vector<vector<int>> dp(word1.size() + 1, vector<int>(word2.size() + 1));
for (int i = 0; i <= word1.size(); i++) dp[i][0] = i;
for (int j = 0; j <= word2.size(); j++) dp[0][j] = j;
2
3
- 确定遍历顺序
从递推公式 dp[i][j] = min(dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 2, min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]) + 1); 和dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1]可以看出dp[i][j]都是根据左上方、正上方、正左方推出来的。
所以遍历的时候一定是从上到下,从左到右,这样保证dp[i][j]可以根据之前计算出来的数值进行计算。
- 举例推导dp数组
以word1:"sea",word2:"eat"为例,推导dp数组状态图如下:
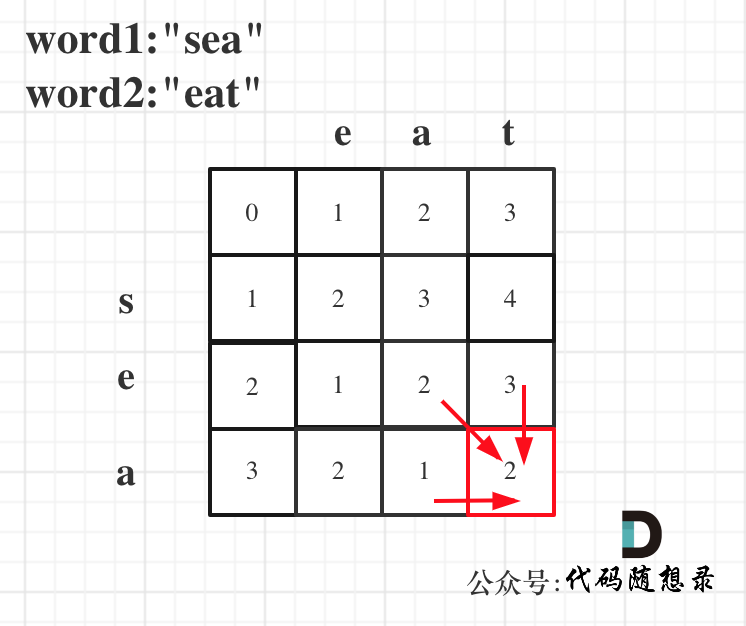
以上分析完毕,代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int minDistance(string word1, string word2) {
vector<vector<int>> dp(word1.size() + 1, vector<int>(word2.size() + 1));
for (int i = 0; i <= word1.size(); i++) dp[i][0] = i;
for (int j = 0; j <= word2.size(); j++) dp[0][j] = j;
for (int i = 1; i <= word1.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= word2.size(); j++) {
if (word1[i - 1] == word2[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
} else {
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i - 1][j] + 1, dp[i][j - 1] + 1);
}
}
}
return dp[word1.size()][word2.size()];
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
- 时间复杂度: O(n * m)
- 空间复杂度: O(n * m)
# 动态规划二
本题和动态规划:1143.最长公共子序列 (opens new window)基本相同,只要求出两个字符串的最长公共子序列长度即可,那么除了最长公共子序列之外的字符都是必须删除的,最后用两个字符串的总长度减去两个最长公共子序列的长度就是删除的最少步数。
代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int minDistance(string word1, string word2) {
vector<vector<int>> dp(word1.size()+1, vector<int>(word2.size()+1, 0));
for (int i=1; i<=word1.size(); i++){
for (int j=1; j<=word2.size(); j++){
if (word1[i-1] == word2[j-1]) dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1;
else dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]);
}
}
return word1.size()+word2.size()-dp[word1.size()][word2.size()]*2;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
- 时间复杂度: O(n * m)
- 空间复杂度: O(n * m)
# 其他语言版本
# Java:
// dp数组中存储word1和word2最长相同子序列的长度
class Solution {
public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
int len1 = word1.length();
int len2 = word2.length();
int[][] dp = new int[len1 + 1][len2 + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= len1; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= len2; j++) {
if (word1.charAt(i - 1) == word2.charAt(j - 1)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
return len1 + len2 - dp[len1][len2] * 2;
}
}
// dp数组中存储需要删除的字符个数
class Solution {
public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
int[][] dp = new int[word1.length() + 1][word2.length() + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < word1.length() + 1; i++) dp[i][0] = i;
for (int j = 0; j < word2.length() + 1; j++) dp[0][j] = j;
for (int i = 1; i < word1.length() + 1; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < word2.length() + 1; j++) {
if (word1.charAt(i - 1) == word2.charAt(j - 1)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
}else{
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 2,
Math.min(dp[i - 1][j] + 1, dp[i][j - 1] + 1));
}
}
}
return dp[word1.length()][word2.length()];
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
//DP - longest common subsequence (用最長公共子序列反推)
class Solution {
public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
char[] char1 = word1.toCharArray();
char[] char2 = word2.toCharArray();
int len1 = char1.length;
int len2 = char2.length;
int dp[][] = new int [len1 + 1][len2 + 1];
for(int i = 1; i <= len1; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= len2; j++){
if(char1[i - 1] == char2[j - 1])
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
else
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
return len1 + len2 - (2 * dp[len1][len2]);//和leetcode 1143只差在這一行。
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# Python:
class Solution:
def minDistance(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:
dp = [[0] * (len(word2)+1) for _ in range(len(word1)+1)]
for i in range(len(word1)+1):
dp[i][0] = i
for j in range(len(word2)+1):
dp[0][j] = j
for i in range(1, len(word1)+1):
for j in range(1, len(word2)+1):
if word1[i-1] == word2[j-1]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]
else:
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i-1][j-1] + 2, dp[i-1][j] + 1, dp[i][j-1] + 1)
return dp[-1][-1]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
版本 2
class Solution(object):
def minDistance(self, word1, word2):
m, n = len(word1), len(word2)
# dp 求解两字符串最长公共子序列
dp = [[0] * (n+1) for _ in range(m+1)]
for i in range(1, m+1):
for j in range(1, n+1):
if word1[i-1] == word2[j-1]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1
else:
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1])
# 删去最长公共子序列以外元素
return m + n - 2 * dp[-1][-1]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# Go:
动态规划一
func minDistance(word1 string, word2 string) int {
dp := make([][]int, len(word1)+1)
for i := 0; i < len(dp); i++ {
dp[i] = make([]int, len(word2)+1)
}
//初始化
for i := 0; i < len(dp); i++ {
dp[i][0] = i
}
for j := 0; j < len(dp[0]); j++ {
dp[0][j] = j
}
for i := 1; i < len(dp); i++ {
for j := 1; j < len(dp[i]); j++ {
if word1[i-1] == word2[j-1] {
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]
} else {
dp[i][j] = min(min(dp[i-1][j]+1, dp[i][j-1]+1), dp[i-1][j-1]+2)
}
}
}
return dp[len(dp)-1][len(dp[0])-1]
}
func min(a, b int) int {
if a < b {
return a
}
return b
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
动态规划二
func minDistance(word1 string, word2 string) int {
dp := make([][]int, len(word1) + 1)
for i := range dp {
dp[i] = make([]int, len(word2) + 1)
}
for i := 1; i <= len(word1); i++ {
for j := 1; j <= len(word2); j++ {
if word1[i-1] == word2[j-1] {
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1
} else {
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1])
}
}
}
return len(word1) + len(word2) - dp[len(word1)][len(word2)] * 2
}
func max(x, y int) int {
if x > y {
return x
}
return y
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# JavaScript:
// 方法一
var minDistance = (word1, word2) => {
let dp = Array.from(new Array(word1.length + 1), () =>
Array(word2.length + 1).fill(0)
);
for (let i = 1; i <= word1.length; i++) {
dp[i][0] = i;
}
for (let j = 1; j <= word2.length; j++) {
dp[0][j] = j;
}
for (let i = 1; i <= word1.length; i++) {
for (let j = 1; j <= word2.length; j++) {
if (word1[i - 1] === word2[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(
dp[i - 1][j] + 1,
dp[i][j - 1] + 1,
dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 2
);
}
}
}
return dp[word1.length][word2.length];
};
// 方法二
var minDistance = function (word1, word2) {
let dp = new Array(word1.length + 1)
.fill(0)
.map((_) => new Array(word2.length + 1).fill(0));
for (let i = 1; i <= word1.length; i++)
for (let j = 1; j <= word2.length; j++)
if (word1[i - 1] === word2[j - 1]) dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
else dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
return word1.length + word2.length - dp[word1.length][word2.length] * 2;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
# TypeScript:
dp版本一:
function minDistance(word1: string, word2: string): number {
/**
dp[i][j]: word1前i个字符,word2前j个字符,所需最小步数
dp[0][0]=0: word1前0个字符为'', word2前0个字符为''
*/
const length1: number = word1.length,
length2: number = word2.length;
const dp: number[][] = new Array(length1 + 1).fill(0)
.map(_ => new Array(length2 + 1).fill(0));
for (let i = 0; i <= length1; i++) {
dp[i][0] = i;
}
for (let i = 0; i <= length2; i++) {
dp[0][i] = i;
}
for (let i = 1; i <= length1; i++) {
for (let j = 1; j <= length2; j++) {
if (word1[i - 1] === word2[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]) + 1;
}
}
}
return dp[length1][length2];
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
dp版本二:
function minDistance(word1: string, word2: string): number {
/**
dp[i][j]: word1前i个字符,word2前j个字符,最长公共子序列的长度
dp[0][0]=0: word1前0个字符为'', word2前0个字符为''
*/
const length1: number = word1.length,
length2: number = word2.length;
const dp: number[][] = new Array(length1 + 1).fill(0)
.map(_ => new Array(length2 + 1).fill(0));
for (let i = 1; i <= length1; i++) {
for (let j = 1; j <= length2; j++) {
if (word1[i - 1] === word2[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j - 1], dp[i - 1][j]);
}
}
}
const maxLen: number = dp[length1][length2];
return length1 + length2 - maxLen * 2;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
Rust:
impl Solution {
pub fn min_distance(word1: String, word2: String) -> i32 {
let mut dp = vec![vec![0; word2.len() + 1]; word1.len() + 1];
for i in 0..word1.len() {
dp[i + 1][0] = i + 1;
}
for j in 0..word2.len() {
dp[0][j + 1] = j + 1;
}
for (i, char1) in word1.chars().enumerate() {
for (j, char2) in word2.chars().enumerate() {
if char1 == char2 {
dp[i + 1][j + 1] = dp[i][j];
continue;
}
dp[i + 1][j + 1] = dp[i][j + 1].min(dp[i + 1][j]) + 1;
}
}
dp[word1.len()][word2.len()] as i32
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
版本 2
impl Solution {
pub fn min_distance(word1: String, word2: String) -> i32 {
let mut dp = vec![vec![0; word2.len() + 1]; word1.len() + 1];
for (i, char1) in word1.chars().enumerate() {
for (j, char2) in word2.chars().enumerate() {
if char1 == char2 {
dp[i + 1][j + 1] = dp[i][j] + 1;
continue;
}
dp[i + 1][j + 1] = dp[i][j + 1].max(dp[i + 1][j]);
}
}
(word1.len() + word2.len() - 2 * dp[word1.len()][word2.len()]) as i32
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
← 48. 不同的子序列 50. 编辑距离 →
