- 做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目) (opens new window)
- 刷算法(两个月高强度学算法) (opens new window)
- 背八股(40天挑战高频面试题) (opens new window)
# 674. 最长连续递增序列
给定一个未经排序的整数数组,找到最长且 连续递增的子序列,并返回该序列的长度。
连续递增的子序列 可以由两个下标 l 和 r(l < r)确定,如果对于每个 l <= i < r,都有 nums[i] < nums[i + 1] ,那么子序列 [nums[l], nums[l + 1], ..., nums[r - 1], nums[r]] 就是连续递增子序列。
示例 1:
- 输入:nums = [1,3,5,4,7]
- 输出:3
- 解释:最长连续递增序列是 [1,3,5], 长度为3。尽管 [1,3,5,7] 也是升序的子序列, 但它不是连续的,因为 5 和 7 在原数组里被 4 隔开。
示例 2:
- 输入:nums = [2,2,2,2,2]
- 输出:1
- 解释:最长连续递增序列是 [2], 长度为1。
提示:
- 0 <= nums.length <= 10^4
- -10^9 <= nums[i] <= 10^9
# 算法公开课
《代码随想录》算法视频公开课 (opens new window):动态规划之子序列问题,重点在于连续!| LeetCode:674.最长连续递增序列 (opens new window),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解。
# 思路
本题相对于昨天的动态规划:300.最长递增子序列 (opens new window)最大的区别在于“连续”。
本题要求的是最长连续递增序列
# 动态规划
动规五部曲分析如下:
- 确定dp数组(dp table)以及下标的含义
dp[i]:以下标i为结尾的连续递增的子序列长度为dp[i]。
注意这里的定义,一定是以下标i为结尾,并不是说一定以下标0为起始位置。
- 确定递推公式
如果 nums[i] > nums[i - 1],那么以 i 为结尾的连续递增的子序列长度 一定等于 以i - 1为结尾的连续递增的子序列长度 + 1 。
即:dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + 1;
注意这里就体现出和动态规划:300.最长递增子序列 (opens new window)的区别!
因为本题要求连续递增子序列,所以就只要比较nums[i]与nums[i - 1],而不用去比较nums[j]与nums[i] (j是在0到i之间遍历)。
既然不用j了,那么也不用两层for循环,本题一层for循环就行,比较nums[i] 和 nums[i - 1]。
这里大家要好好体会一下!
- dp数组如何初始化
以下标i为结尾的连续递增的子序列长度最少也应该是1,即就是nums[i]这一个元素。
所以dp[i]应该初始1;
- 确定遍历顺序
从递推公式上可以看出, dp[i + 1]依赖dp[i],所以一定是从前向后遍历。
本文在确定递推公式的时候也说明了为什么本题只需要一层for循环,代码如下:
for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if (nums[i] > nums[i - 1]) { // 连续记录
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + 1;
}
}
2
3
4
5
- 举例推导dp数组
已输入nums = [1,3,5,4,7]为例,dp数组状态如下:
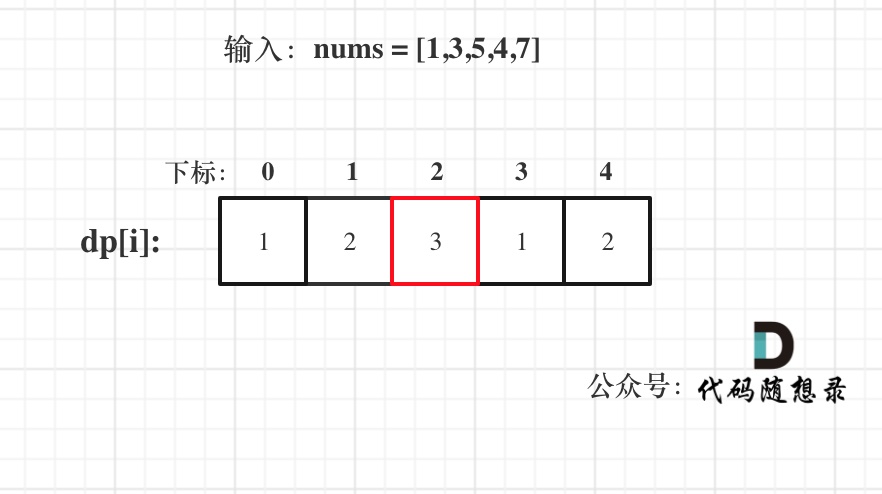
注意这里要取dp[i]里的最大值,所以dp[2]才是结果!
以上分析完毕,C++代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int findLengthOfLCIS(vector<int>& nums) {
if (nums.size() == 0) return 0;
int result = 1;
vector<int> dp(nums.size() ,1);
for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if (nums[i] > nums[i - 1]) { // 连续记录
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + 1;
}
if (dp[i] > result) result = dp[i];
}
return result;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
# 贪心
这道题目也可以用贪心来做,也就是遇到nums[i] > nums[i - 1]的情况,count就++,否则count为1,记录count的最大值就可以了。
代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int findLengthOfLCIS(vector<int>& nums) {
if (nums.size() == 0) return 0;
int result = 1; // 连续子序列最少也是1
int count = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if (nums[i] > nums[i - 1]) { // 连续记录
count++;
} else { // 不连续,count从头开始
count = 1;
}
if (count > result) result = count;
}
return result;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
# 总结
本题也是动规里子序列问题的经典题目,但也可以用贪心来做,大家也会发现贪心好像更简单一点,而且空间复杂度仅是O(1)。
在动规分析中,关键是要理解和动态规划:300.最长递增子序列 (opens new window)的区别。
要联动起来,才能理解递增子序列怎么求,递增连续子序列又要怎么求。
概括来说:不连续递增子序列的跟前0-i 个状态有关,连续递增的子序列只跟前一个状态有关
本篇我也把区别所在之处重点介绍了,关键在递推公式和遍历方法上,大家可以仔细体会一波!
# 其他语言版本
# Java:
动态规划:
/**
* 1.dp[i] 代表当前下标最大连续值
* 2.递推公式 if(nums[i+1]>nums[i]) dp[i+1] = dp[i]+1
* 3.初始化 都为1
* 4.遍历方向,从其那往后
* 5.结果推导 。。。。
* @param nums
* @return
*/
public static int findLengthOfLCIS(int[] nums) {
int[] dp = new int[nums.length];
for (int i = 0; i < dp.length; i++) {
dp[i] = 1;
}
int res = 1;
//可以注意到,這邊的 i 是從 0 開始,所以會出現和卡哥的C++ code有差異的地方,在一些地方會看到有 i + 1 的偏移。
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {
if (nums[i + 1] > nums[i]) {
dp[i + 1] = dp[i] + 1;
}
res = res > dp[i + 1] ? res : dp[i + 1];
}
return res;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
动态规划状态压缩
class Solution {
public int findLengthOfLCIS(int[] nums) {
// 记录以 前一个元素结尾的最长连续递增序列的长度 和 以当前 结尾的......
int beforeOneMaxLen = 1, currentMaxLen = 0;
// res 赋最小值返回的最小值1
int res = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i ++) {
currentMaxLen = nums[i] > nums[i - 1] ? beforeOneMaxLen + 1 : 1;
beforeOneMaxLen = currentMaxLen;
res = Math.max(res, currentMaxLen);
}
return res;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
贪心法:
public static int findLengthOfLCIS(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0) return 0;
int res = 1; // 连续子序列最少也是1
int count = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {
if (nums[i + 1] > nums[i]) { // 连续记录
count++;
} else { // 不连续,count从头开始
count = 1;
}
if (count > res) res = count;
}
return res;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# Python:
DP
class Solution:
def findLengthOfLCIS(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
if len(nums) == 0:
return 0
result = 1
dp = [1] * len(nums)
for i in range(len(nums)-1):
if nums[i+1] > nums[i]: #连续记录
dp[i+1] = dp[i] + 1
result = max(result, dp[i+1])
return result
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
DP(优化版)
class Solution:
def findLengthOfLCIS(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
if not nums:
return 0
max_length = 1
current_length = 1
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
if nums[i] > nums[i - 1]:
current_length += 1
max_length = max(max_length, current_length)
else:
current_length = 1
return max_length
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
贪心
class Solution:
def findLengthOfLCIS(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
if len(nums) == 0:
return 0
result = 1 #连续子序列最少也是1
count = 1
for i in range(len(nums)-1):
if nums[i+1] > nums[i]: #连续记录
count += 1
else: #不连续,count从头开始
count = 1
result = max(result, count)
return result
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# Go:
动态规划:
func findLengthOfLCIS(nums []int) int {
if len(nums) == 0 {return 0}
res, count := 1, 1
for i := 0; i < len(nums)-1; i++ {
if nums[i+1] > nums[i] {
count++
}else {
count = 1
}
if count > res {
res = count
}
}
return res
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
贪心算法:
func findLengthOfLCIS(nums []int) int {
if len(nums) == 0 {return 0}
dp := make([]int, len(nums))
for i := 0; i < len(dp); i++ {
dp[i] = 1
}
res := 1
for i := 0; i < len(nums)-1; i++ {
if nums[i+1] > nums[i] {
dp[i+1] = dp[i] + 1
}
if dp[i+1] > res {
res = dp[i+1]
}
}
return res
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# Rust:
动态规划
pub fn find_length_of_lcis(nums: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
if nums.is_empty() {
return 0;
}
let mut result = 1;
let mut dp = vec![1; nums.len()];
for i in 1..nums.len() {
if nums[i - 1] < nums[i] {
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + 1;
result = result.max(dp[i]);
}
}
result
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
贪心
impl Solution {
pub fn find_length_of_lcis(nums: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
let (mut res, mut count) = (1, 1);
for i in 1..nums.len() {
if nums[i] > nums[i - 1] {
count += 1;
res = res.max(count);
continue;
}
count = 1;
}
res
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# JavaScript:
动态规划:
const findLengthOfLCIS = (nums) => {
let dp = new Array(nums.length).fill(1);
for(let i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {
if(nums[i+1] > nums[i]) {
dp[i+1] = dp[i]+ 1;
}
}
return Math.max(...dp);
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
贪心法:
const findLengthOfLCIS = (nums) => {
if(nums.length === 1) {
return 1;
}
let maxLen = 1;
let curMax = 1;
let cur = nums[0];
for(let num of nums) {
if(num > cur) {
curMax += 1;
maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, curMax);
} else {
curMax = 1;
}
cur = num;
}
return maxLen;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# TypeScript:
动态规划:
function findLengthOfLCIS(nums: number[]): number {
/**
dp[i]: 前i个元素,以nums[i]结尾,最长连续子序列的长度
*/
const dp: number[] = new Array(nums.length).fill(1);
let resMax: number = 1;
for (let i = 1, length = nums.length; i < length; i++) {
if (nums[i] > nums[i - 1]) {
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + 1;
}
resMax = Math.max(resMax, dp[i]);
}
return resMax;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
贪心:
function findLengthOfLCIS(nums: number[]): number {
let resMax: number = 1;
let count: number = 1;
for (let i = 0, length = nums.length; i < length - 1; i++) {
if (nums[i] < nums[i + 1]) {
count++;
} else {
count = 1;
}
resMax = Math.max(resMax, count);
}
return resMax;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# C:
动态规划:
int findLengthOfLCIS(int* nums, int numsSize) {
if(numsSize == 0){
return 0;
}
int dp[numsSize];
for(int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++){
dp[i] = 1;
}
int result = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < numsSize; ++i) {
if(nums[i] > nums[i - 1]){
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + 1;
}
if(dp[i] > result){
result = dp[i];
}
}
return result;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
贪心:
int findLengthOfLCIS(int* nums, int numsSize) {
int result = 1;
int count = 1;
if(numsSize == 0){
return result;
}
for (int i = 1; i < numsSize; ++i) {
if(nums[i] > nums[i - 1]){
count++;
} else{
count = 1;
}
if(count > result){
result = count;
}
}
return result;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# Cangjie
func findLengthOfLCIS(nums: Array<Int64>): Int64 {
let n = nums.size
if (n <= 1) {
return n
}
let dp = Array(n, repeat: 1)
var res = 0
for (i in 1..n) {
if (nums[i] > nums[i - 1]) {
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + 1
}
res = max(res, dp[i])
}
return res
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
