参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们受益!
# 100. 岛屿的最大面积
卡码网题目链接(ACM模式) (opens new window)
题目描述
给定一个由 1(陆地)和 0(水)组成的矩阵,计算岛屿的最大面积。岛屿面积的计算方式为组成岛屿的陆地的总数。岛屿由水平方向或垂直方向上相邻的陆地连接而成,并且四周都是水域。你可以假设矩阵外均被水包围。
输入描述
第一行包含两个整数 N, M,表示矩阵的行数和列数。后续 N 行,每行包含 M 个数字,数字为 1 或者 0,表示岛屿的单元格。
输出描述
输出一个整数,表示岛屿的最大面积。如果不存在岛屿,则输出 0。
输入示例
4 5
1 1 0 0 0
1 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 1 1
2
3
4
5
输出示例
4
提示信息
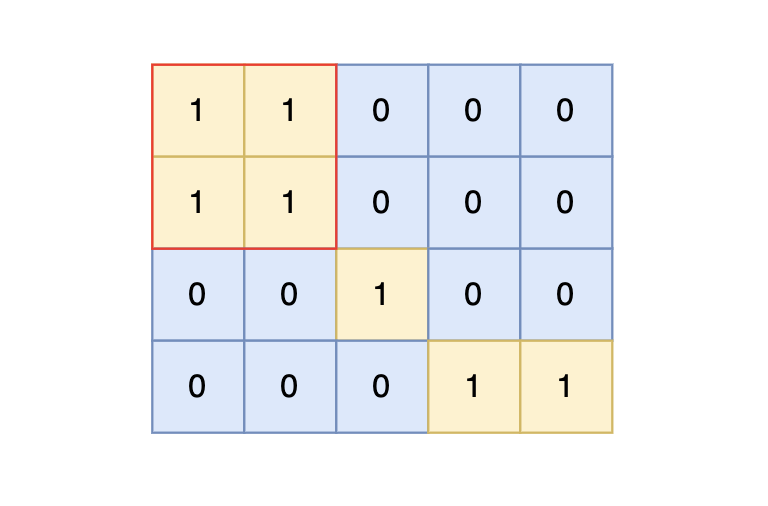
样例输入中,岛屿的最大面积为 4。
数据范围:
- 1 <= M, N <= 50。
# 思路
《代码随想录》算法视频公开课 (opens new window):图论:深搜也有陷阱啊!! | 深搜优先搜索 | 卡码网:100.岛屿的最大面积 (opens new window),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解。
注意题目中每座岛屿只能由水平方向和/或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成。
也就是说斜角度链接是不算了, 例如示例二,是三个岛屿,如图:
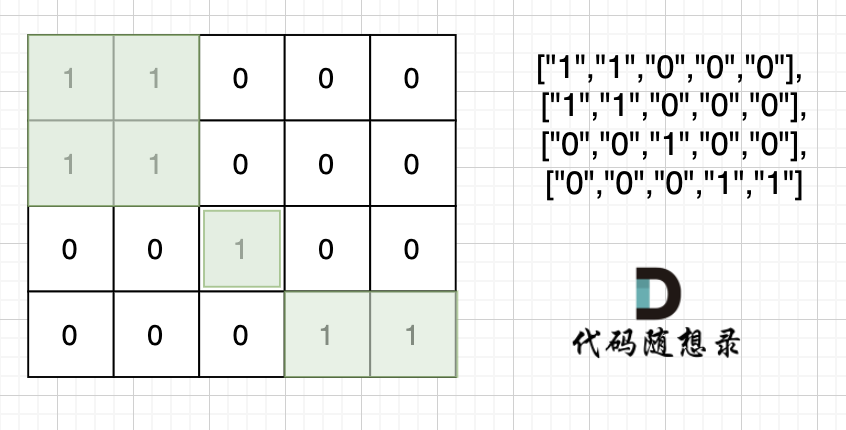
这道题目也是 dfs bfs基础类题目,就是搜索每个岛屿上“1”的数量,然后取一个最大的。
本题思路上比较简单,难点其实都是 dfs 和 bfs的理论基础,关于理论基础我在这里都有详细讲解 :
# DFS
很多同学写dfs其实也是凭感觉来的,有的时候dfs函数中写终止条件才能过,有的时候 dfs函数不写终止添加也能过!
这里其实涉及到dfs的两种写法。
写法一,dfs处理当前节点的相邻节点,即在主函数遇到岛屿就计数为1,dfs处理接下来的相邻陆地
// 版本一
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int count;
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextx = x + dir[i][0];
int nexty = y + dir[i][1];
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == 1) { // 没有访问过的 同时 是陆地的
visited[nextx][nexty] = true;
count++;
dfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty);
}
}
}
int main() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<vector<int>> grid(n, vector<int>(m, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
cin >> grid[i][j];
}
}
vector<vector<bool>> visited(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1) {
count = 1; // 因为dfs处理下一个节点,所以这里遇到陆地了就先计数,dfs处理接下来的相邻陆地
visited[i][j] = true;
dfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 true
result = max(result, count);
}
}
}
cout << result << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
写法二,dfs处理当前节点,即在主函数遇到岛屿就计数为0,dfs处理接下来的全部陆地
dfs
// 版本二
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int count;
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {
if (visited[x][y] || grid[x][y] == 0) return; // 终止条件:访问过的节点 或者 遇到海水
visited[x][y] = true; // 标记访问过
count++;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextx = x + dir[i][0];
int nexty = y + dir[i][1];
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
dfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty);
}
}
int main() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<vector<int>> grid(n, vector<int>(m, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
cin >> grid[i][j];
}
}
vector<vector<bool>> visited = vector<vector<bool>>(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1) {
count = 0; // 因为dfs处理当前节点,所以遇到陆地计数为0,进dfs之后在开始从1计数
dfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 true
result = max(result, count);
}
}
}
cout << result << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
大家通过注释可以发现,两种写法,版本一,在主函数遇到陆地就计数为1,接下来的相邻陆地都在dfs中计算。
版本二 在主函数遇到陆地 计数为0,也就是不计数,陆地数量都去dfs里做计算。
这也是为什么大家看了很多 dfs的写法 ,发现写法怎么都不一样呢? 其实这就是根本原因。
# BFS
关于广度优先搜索,如果大家还不了解的话,看这里:广度优先搜索精讲
本题BFS代码如下:
class Solution {
private:
int count;
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
void bfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {
queue<int> que;
que.push(x);
que.push(y);
visited[x][y] = true; // 加入队列就意味节点是陆地可到达的点
count++;
while(!que.empty()) {
int xx = que.front();que.pop();
int yy = que.front();que.pop();
for (int i = 0 ;i < 4; i++) {
int nextx = xx + dir[i][0];
int nexty = yy + dir[i][1];
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界
if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == 1) { // 节点没有被访问过且是陆地
visited[nextx][nexty] = true;
count++;
que.push(nextx);
que.push(nexty);
}
}
}
}
public:
int maxAreaOfIsland(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int n = grid.size(), m = grid[0].size();
vector<vector<bool>> visited = vector<vector<bool>>(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1) {
count = 0;
bfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 true
result = max(result, count);
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
# 其他语言版本
# Java
import java.util.*;
import java.math.*;
/**
* DFS版
*/
public class Main{
static final int[][] dir={{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}};
static int result=0;
static int count=0;
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
int m = scanner.nextInt();
int[][] map = new int[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
map[i][j]=scanner.nextInt();
}
}
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if(!visited[i][j]&&map[i][j]==1){
count=0;
dfs(map,visited,i,j);
result= Math.max(count, result);
}
}
}
System.out.println(result);
}
static void dfs(int[][] map,boolean[][] visited,int x,int y){
count++;
visited[x][y]=true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextX=x+dir[i][0];
int nextY=y+dir[i][1];
//水或者已经访问过的跳过
if(nextX<0||nextY<0
||nextX>=map.length||nextY>=map[0].length
||visited[nextX][nextY]||map[nextX][nextY]==0)continue;
dfs(map,visited,nextX,nextY);
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
import java.util.*;
import java.math.*;
/**
* BFS版
*/
public class Main {
static class Node {
int x;
int y;
public Node(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
static final int[][] dir = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
static int result = 0;
static int count = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
int m = scanner.nextInt();
int[][] map = new int[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
map[i][j] = scanner.nextInt();
}
}
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (!visited[i][j] && map[i][j] == 1) {
count = 0;
bfs(map, visited, i, j);
result = Math.max(count, result);
}
}
}
System.out.println(result);
}
static void bfs(int[][] map, boolean[][] visited, int x, int y) {
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(new Node(x, y));
visited[x][y] = true;
count++;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Node node = q.remove();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextX = node.x + dir[i][0];
int nextY = node.y + dir[i][1];
if (nextX < 0 || nextY < 0 || nextX >= map.length || nextY >= map[0].length || visited[nextX][nextY] || map[nextX][nextY] == 0)
continue;
q.add(new Node(nextX, nextY));
visited[nextX][nextY] = true;
count++;
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
# Python
DFS
# 四个方向
position = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1], [-1, 0]]
count = 0
def dfs(grid, visited, x, y):
"""
深度优先搜索,对一整块陆地进行标记
"""
global count # 定义全局变量,便于传递count值
for i, j in position:
cur_x = x + i
cur_y = y + j
# 下标越界,跳过
if cur_x < 0 or cur_x >= len(grid) or cur_y < 0 or cur_y >= len(grid[0]):
continue
if not visited[cur_x][cur_y] and grid[cur_x][cur_y] == 1:
visited[cur_x][cur_y] = True
count += 1
dfs(grid, visited, cur_x, cur_y)
n, m = map(int, input().split())
# 邻接矩阵
grid = []
for i in range(n):
grid.append(list(map(int, input().split())))
# 访问表
visited = [[False] * m for _ in range(n)]
result = 0 # 记录最终结果
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if grid[i][j] == 1 and not visited[i][j]:
count = 1
visited[i][j] = True
dfs(grid, visited, i, j)
result = max(count, result)
print(result)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
BFS
from collections import deque
position = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1], [-1, 0]] # 四个方向
count = 0
def bfs(grid, visited, x, y):
"""
广度优先搜索对陆地进行标记
"""
global count # 声明全局变量
que = deque()
que.append([x, y])
while que:
cur_x, cur_y = que.popleft()
for i, j in position:
next_x = cur_x + i
next_y = cur_y + j
# 下标越界,跳过
if next_x < 0 or next_x >= len(grid) or next_y < 0 or next_y >= len(grid[0]):
continue
if grid[next_x][next_y] == 1 and not visited[next_x][next_y]:
visited[next_x][next_y] = True
count += 1
que.append([next_x, next_y])
n, m = map(int, input().split())
# 邻接矩阵
grid = []
for i in range(n):
grid.append(list(map(int, input().split())))
visited = [[False] * m for _ in range(n)] # 访问表
result = 0 # 记录最终结果
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if grid[i][j] == 1 and not visited[i][j]:
count = 1
visited[i][j] = True
bfs(grid, visited, i, j)
res = max(result, count)
print(result)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
# Go
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
var count int
var dir = [][]int{{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}} // 四个方向
func dfs(grid [][]int, visited [][]bool, x, y int) {
for i := 0; i < 4; i++ {
nextx := x + dir[i][0]
nexty := y + dir[i][1]
if nextx < 0 || nextx >= len(grid) || nexty < 0 || nexty >= len(grid[0]) {
continue // 越界了,直接跳过
}
if !visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == 1 { // 没有访问过的 同时 是陆地的
visited[nextx][nexty] = true
count++
dfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty)
}
}
}
func main() {
var n, m int
fmt.Scan(&n, &m)
grid := make([][]int, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
grid[i] = make([]int, m)
for j := 0; j < m; j++ {
fmt.Scan(&grid[i][j])
}
}
visited := make([][]bool, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
visited[i] = make([]bool, m)
}
result := 0
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
for j := 0; j < m; j++ {
if !visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1 {
count = 1 // 因为dfs处理下一个节点,所以这里遇到陆地了就先计数,dfs处理接下来的相邻陆地
visited[i][j] = true
dfs(grid, visited, i, j)
if count > result {
result = count
}
}
}
}
fmt.Println(result)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
# Rust
DFS
use std::io;
use std::cmp;
// 定义四个方向
const DIRECTIONS: [(i32, i32); 4] = [(0, 1), (1, 0), (-1, 0), (0, -1)];
fn dfs(grid: &Vec<Vec<i32>>, visited: &mut Vec<Vec<bool>>, x: usize, y: usize, count: &mut i32) {
if visited[x][y] || grid[x][y] == 0 {
return; // 终止条件:已访问或者遇到海水
}
visited[x][y] = true; // 标记已访问
*count += 1;
for &(dx, dy) in DIRECTIONS.iter() {
let new_x = x as i32 + dx;
let new_y = y as i32 + dy;
// 检查边界条件
if new_x >= 0 && new_x < grid.len() as i32 && new_y >= 0 && new_y < grid[0].len() as i32 {
dfs(grid, visited, new_x as usize, new_y as usize, count);
}
}
}
fn main() {
let mut input = String::new();
// 读取 n 和 m
io::stdin().read_line(&mut input);
let dims: Vec<usize> = input.trim().split_whitespace().map(|s| s.parse().unwrap()).collect();
let (n, m) = (dims[0], dims[1]);
// 读取 grid
let mut grid = vec![];
for _ in 0..n {
input.clear();
io::stdin().read_line(&mut input);
let row: Vec<i32> = input.trim().split_whitespace().map(|s| s.parse().unwrap()).collect();
grid.push(row);
}
// 初始化访问记录
let mut visited = vec![vec![false; m]; n];
let mut result = 0;
// 遍历所有格子
for i in 0..n {
for j in 0..m {
if !visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1 {
let mut count = 0;
dfs(&grid, &mut visited, i, j, &mut count);
result = cmp::max(result, count);
}
}
}
// 输出结果
println!("{}", result);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
BFS
use std::io;
use std::collections::VecDeque;
// 定义四个方向
const DIRECTIONS: [(i32, i32); 4] = [(0, 1), (1, 0), (-1, 0), (0, -1)];
fn bfs(grid: &Vec<Vec<i32>>, visited: &mut Vec<Vec<bool>>, x: usize, y: usize) -> i32 {
let mut count = 0;
let mut queue = VecDeque::new();
queue.push_back((x, y));
visited[x][y] = true; // 标记已访问
while let Some((cur_x, cur_y)) = queue.pop_front() {
count += 1; // 增加计数
for &(dx, dy) in DIRECTIONS.iter() {
let new_x = cur_x as i32 + dx;
let new_y = cur_y as i32 + dy;
// 检查边界条件
if new_x >= 0 && new_x < grid.len() as i32 && new_y >= 0 && new_y < grid[0].len() as i32 {
let new_x_usize = new_x as usize;
let new_y_usize = new_y as usize;
// 如果未访问且是陆地,加入队列
if !visited[new_x_usize][new_y_usize] && grid[new_x_usize][new_y_usize] == 1 {
visited[new_x_usize][new_y_usize] = true; // 标记已访问
queue.push_back((new_x_usize, new_y_usize));
}
}
}
}
count
}
fn main() {
let mut input = String::new();
// 读取 n 和 m
io::stdin().read_line(&mut input).expect("Failed to read line");
let dims: Vec<usize> = input.trim().split_whitespace().map(|s| s.parse().unwrap()).collect();
let (n, m) = (dims[0], dims[1]);
// 读取 grid
let mut grid = vec![];
for _ in 0..n {
input.clear();
io::stdin().read_line(&mut input).expect("Failed to read line");
let row: Vec<i32> = input.trim().split_whitespace().map(|s| s.parse().unwrap()).collect();
grid.push(row);
}
// 初始化访问记录
let mut visited = vec![vec![false; m]; n];
let mut result = 0;
// 遍历所有格子
for i in 0..n {
for j in 0..m {
if !visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1 {
let count = bfs(&grid, &mut visited, i, j);
result = result.max(count);
}
}
}
// 输出结果
println!("{}", result);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
# JavaScript
// 广搜版
const r1 = require('readline').createInterface({ input: process.stdin });
// 创建readline接口
let iter = r1[Symbol.asyncIterator]();
// 创建异步迭代器
const readline = async () => (await iter.next()).value;
let graph // 地图
let N, M // 地图大小
let visited // 访问过的节点
let result = 0 // 最大岛屿面积
let count = 0 // 岛屿内节点数
const dir = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1], [-1, 0]] //方向
// 读取输入,初始化地图
const initGraph = async () => {
let line = await readline();
[N, M] = line.split(' ').map(Number);
graph = new Array(N).fill(0).map(() => new Array(M).fill(0))
visited = new Array(N).fill(false).map(() => new Array(M).fill(false))
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
line = await readline()
line = line.split(' ').map(Number)
for (let j = 0; j < M; j++) {
graph[i][j] = line[j]
}
}
}
/**
* @description: 从(x, y)开始广度优先遍历
* @param {*} graph 地图
* @param {*} visited 访问过的节点
* @param {*} x 开始搜索节点的下标
* @param {*} y 开始搜索节点的下标
* @return {*}
*/
const bfs = (graph, visited, x, y) => {
let queue = []
queue.push([x, y])
count++
visited[x][y] = true //只要加入队列就立刻标记为访问过
while (queue.length) {
let [xx, yy] = queue.shift()
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
let nextx = xx + dir[i][0]
let nexty = yy + dir[i][1]
if(nextx < 0 || nextx >= N || nexty < 0 || nexty >= M) continue
if(!visited[nextx][nexty] && graph[nextx][nexty] === 1){
queue.push([nextx, nexty])
count++
visited[nextx][nexty] = true
}
}
}
}
(async function () {
// 读取输入,初始化地图
await initGraph()
// 统计最大岛屿面积
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < M; j++) {
if (!visited[i][j] && graph[i][j] === 1) { //遇到没有访问过的陆地
// 重新计算面积
count = 0
// 广度优先遍历,统计岛屿内节点数,并将岛屿标记为已访问
bfs(graph, visited, i, j)
// 更新最大岛屿面积
result = Math.max(result, count)
}
}
}
console.log(result);
})()
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
// 深搜版
const r1 = require('readline').createInterface({ input: process.stdin });
// 创建readline接口
let iter = r1[Symbol.asyncIterator]();
// 创建异步迭代器
const readline = async () => (await iter.next()).value;
let graph // 地图
let N, M // 地图大小
let visited // 访问过的节点
let result = 0 // 最大岛屿面积
let count = 0 // 岛屿内节点数
const dir = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1], [-1, 0]] //方向
// 读取输入,初始化地图
const initGraph = async () => {
let line = await readline();
[N, M] = line.split(' ').map(Number);
graph = new Array(N).fill(0).map(() => new Array(M).fill(0))
visited = new Array(N).fill(false).map(() => new Array(M).fill(false))
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
line = await readline()
line = line.split(' ').map(Number)
for (let j = 0; j < M; j++) {
graph[i][j] = line[j]
}
}
}
/**
* @description: 从(x, y)开始深度优先遍历
* @param {*} graph 地图
* @param {*} visited 访问过的节点
* @param {*} x 开始搜索节点的下标
* @param {*} y 开始搜索节点的下标
* @return {*}
*/
const dfs = (graph, visited, x, y) => {
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
let nextx = x + dir[i][0]
let nexty = y + dir[i][1]
if(nextx < 0 || nextx >= N || nexty < 0 || nexty >= M) continue
if(!visited[nextx][nexty] && graph[nextx][nexty] === 1){
count++
visited[nextx][nexty] = true
dfs(graph, visited, nextx, nexty)
}
}
}
(async function () {
// 读取输入,初始化地图
await initGraph()
// 统计最大岛屿面积
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < M; j++) {
if (!visited[i][j] && graph[i][j] === 1) { //遇到没有访问过的陆地
// 重新计算面积
count = 1
visited[i][j] = true
// 深度优先遍历,统计岛屿内节点数,并将岛屿标记为已访问
dfs(graph, visited, i, j)
// 更新最大岛屿面积
result = Math.max(result, count)
}
}
}
console.log(result);
})()
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
# TypeScript
# PhP
<?php
function dfs(&$grid, &$visited, $x, $y, &$count, &$dir) {
for ($i = 0; $i < 4; $i++) {
$nextx = $x + $dir[$i][0];
$nexty = $y + $dir[$i][1];
if ($nextx < 0 || $nextx >= count($grid) || $nexty < 0 || $nexty >= count($grid[0])) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
if (!$visited[$nextx][$nexty] && $grid[$nextx][$nexty] == 1) { // 没有访问过的 同时 是陆地的
$visited[$nextx][$nexty] = true;
$count++;
dfs($grid, $visited, $nextx, $nexty, $count, $dir);
}
}
}
// Main function
function main() {
$input = trim(fgets(STDIN));
list($n, $m) = explode(' ', $input);
$grid = [];
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++) {
$input = trim(fgets(STDIN));
$grid[] = array_map('intval', explode(' ', $input));
}
$visited = [];
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++) {
$visited[] = array_fill(0, $m, false);
}
$result = 0;
$count = 0;
$dir = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, -1]]; // 四个方向
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++) {
for ($j = 0; $j < $m; $j++) {
if (!$visited[$i][$j] && $grid[$i][$j] == 1) {
$count = 1; // 因为dfs处理下一个节点,所以这里遇到陆地了就先计数,dfs处理接下来的相邻陆地
$visited[$i][$j] = true;
dfs($grid, $visited, $i, $j, $count, $dir); // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 true
$result = max($result, $count);
}
}
}
echo $result . "\n";
}
main();
?>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55

评论
验证登录状态...