- 做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目) (opens new window)
- 刷算法(两个月高强度学算法) (opens new window)
- 背八股(40天挑战高频面试题) (opens new window)
工作上一定没人这么搞,但是考察对栈、队列理解程度的好题
# 232.用栈实现队列
使用栈实现队列的下列操作:
push(x) -- 将一个元素放入队列的尾部。
pop() -- 从队列首部移除元素。
peek() -- 返回队列首部的元素。
empty() -- 返回队列是否为空。
示例:
MyQueue queue = new MyQueue();
queue.push(1);
queue.push(2);
queue.peek(); // 返回 1
queue.pop(); // 返回 1
queue.empty(); // 返回 false
2
3
4
5
6
说明:
- 你只能使用标准的栈操作 -- 也就是只有 push to top, peek/pop from top, size, 和 is empty 操作是合法的。
- 你所使用的语言也许不支持栈。你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个栈,只要是标准的栈操作即可。
- 假设所有操作都是有效的 (例如,一个空的队列不会调用 pop 或者 peek 操作)。
# 算法公开课
《代码随想录》算法视频公开课 (opens new window):栈的基本操作! | LeetCode:232.用栈实现队列 (opens new window),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解。
# 思路
这是一道模拟题,不涉及到具体算法,考察的就是对栈和队列的掌握程度。
使用栈来模拟队列的行为,如果仅仅用一个栈,是一定不行的,所以需要两个栈一个输入栈,一个输出栈,这里要注意输入栈和输出栈的关系。
下面动画模拟以下队列的执行过程:
执行语句:
queue.push(1);
queue.push(2);
queue.pop(); 注意此时的输出栈的操作
queue.push(3);
queue.push(4);
queue.pop();
queue.pop();注意此时的输出栈的操作
queue.pop();
queue.empty();
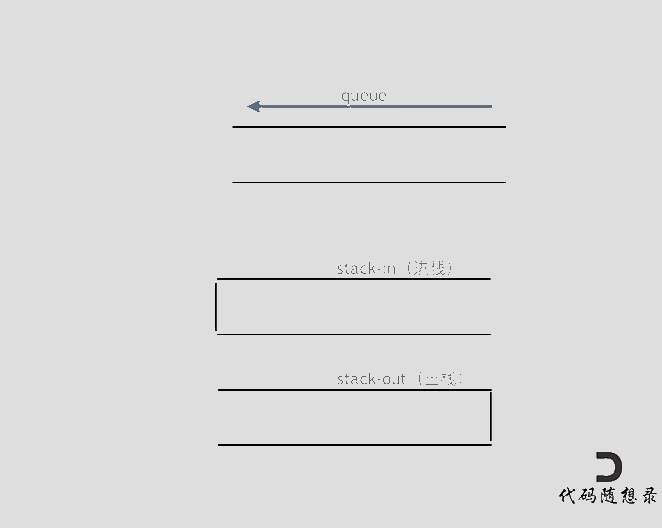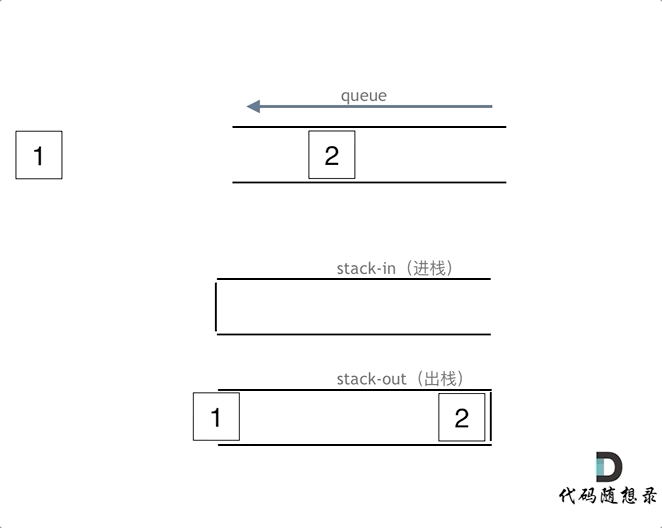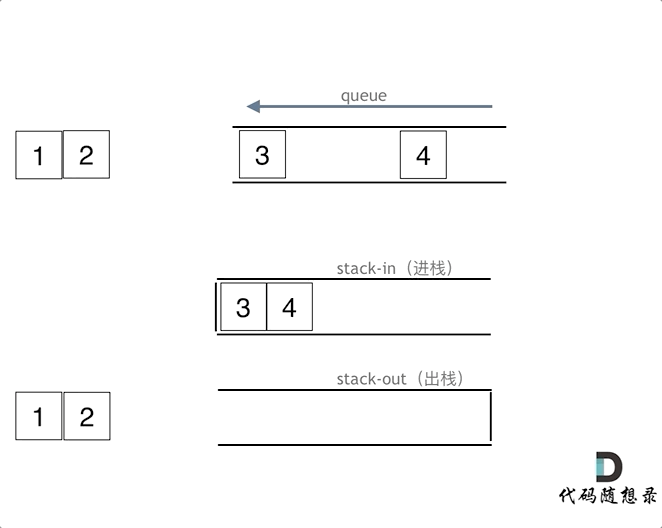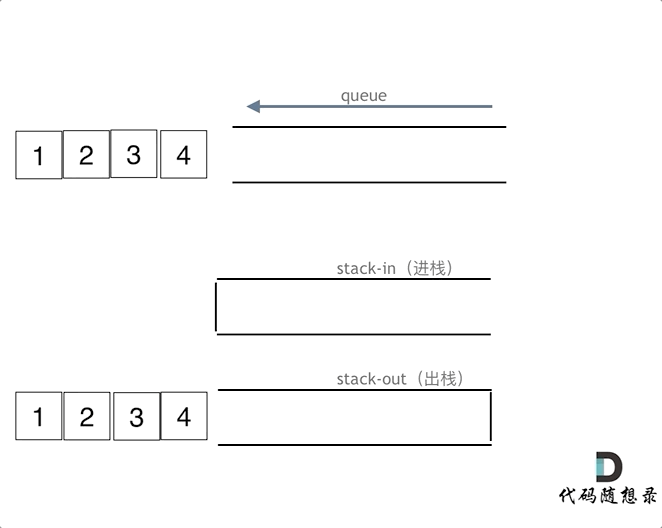
在push数据的时候,只要数据放进输入栈就好,但在pop的时候,操作就复杂一些,输出栈如果为空,就把进栈数据全部导入进来(注意是全部导入),再从出栈弹出数据,如果输出栈不为空,则直接从出栈弹出数据就可以了。
最后如何判断队列为空呢?如果进栈和出栈都为空的话,说明模拟的队列为空了。
在代码实现的时候,会发现pop() 和 peek()两个函数功能类似,代码实现上也是类似的,可以思考一下如何把代码抽象一下。
C++代码如下:
class MyQueue {
public:
stack<int> stIn;
stack<int> stOut;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyQueue() {
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
void push(int x) {
stIn.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
int pop() {
// 只有当stOut为空的时候,再从stIn里导入数据(导入stIn全部数据)
if (stOut.empty()) {
// 从stIn导入数据直到stIn为空
while(!stIn.empty()) {
stOut.push(stIn.top());
stIn.pop();
}
}
int result = stOut.top();
stOut.pop();
return result;
}
/** Get the front element. */
int peek() {
int res = this->pop(); // 直接使用已有的pop函数
stOut.push(res); // 因为pop函数弹出了元素res,所以再添加回去
return res;
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
bool empty() {
return stIn.empty() && stOut.empty();
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
- 时间复杂度: 都为O(1)。pop和peek看起来像O(n),实际上一个循环n会被使用n次,最后还是O(1)。
- 空间复杂度: O(n)
# 拓展
可以看出peek()的实现,直接复用了pop(), 要不然,对stOut判空的逻辑又要重写一遍。
再多说一些代码开发上的习惯问题,在工业级别代码开发中,最忌讳的就是 实现一个类似的函数,直接把代码粘过来改一改就完事了。
这样的项目代码会越来越乱,一定要懂得复用,功能相近的函数要抽象出来,不要大量的复制粘贴,很容易出问题!(踩过坑的人自然懂)
工作中如果发现某一个功能自己要经常用,同事们可能也会用到,自己就花点时间把这个功能抽象成一个好用的函数或者工具类,不仅自己方便,也方便了同事们。
同事们就会逐渐认可你的工作态度和工作能力,自己的口碑都是这么一点一点积累起来的!在同事圈里口碑起来了之后,你就发现自己走上了一个正循环,以后的升职加薪才少不了你!
# 其他语言版本
# Java:
class MyQueue {
Stack<Integer> stackIn;
Stack<Integer> stackOut;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyQueue() {
stackIn = new Stack<>(); // 负责进栈
stackOut = new Stack<>(); // 负责出栈
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
public void push(int x) {
stackIn.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
dumpstackIn();
return stackOut.pop();
}
/** Get the front element. */
public int peek() {
dumpstackIn();
return stackOut.peek();
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return stackIn.isEmpty() && stackOut.isEmpty();
}
// 如果stackOut为空,那么将stackIn中的元素全部放到stackOut中
private void dumpstackIn(){
if (!stackOut.isEmpty()) return;
while (!stackIn.isEmpty()){
stackOut.push(stackIn.pop());
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
# Python:
class MyQueue:
def __init__(self):
"""
in主要负责push,out主要负责pop
"""
self.stack_in = []
self.stack_out = []
def push(self, x: int) -> None:
"""
有新元素进来,就往in里面push
"""
self.stack_in.append(x)
def pop(self) -> int:
"""
Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element.
"""
if self.empty():
return None
if self.stack_out:
return self.stack_out.pop()
else:
for i in range(len(self.stack_in)):
self.stack_out.append(self.stack_in.pop())
return self.stack_out.pop()
def peek(self) -> int:
"""
Get the front element.
"""
ans = self.pop()
self.stack_out.append(ans)
return ans
def empty(self) -> bool:
"""
只要in或者out有元素,说明队列不为空
"""
return not (self.stack_in or self.stack_out)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
# Go:
// 通过切片实现一个栈
// 由于只是辅助实现算法题目,因此不做异常情况处理
type MyStack []int
func (s *MyStack) Push(v int) {
*s = append(*s, v)
}
func (s *MyStack) Pop() int {
val := (*s)[len(*s)-1]
*s = (*s)[:len(*s)-1]
return val
}
func (s *MyStack) Peek() int {
return (*s)[len(*s)-1]
}
func (s *MyStack) Size() int {
return len(*s)
}
func (s *MyStack) Empty() bool {
return s.Size() == 0
}
// ---------- 分界线 ----------
type MyQueue struct {
stackIn *MyStack
stackOut *MyStack
}
func Constructor() MyQueue {
return MyQueue {
stackIn: &MyStack{},
stackOut: &MyStack{},
}
}
func (this *MyQueue) Push(x int) {
this.stackIn.Push(x)
}
func (this *MyQueue) Pop() int {
this.fillStackOut()
return this.stackOut.Pop()
}
func (this *MyQueue) Peek() int {
this.fillStackOut()
return this.stackOut.Peek()
}
func (this *MyQueue) Empty() bool {
return this.stackIn.Empty() && this.stackOut.Empty()
}
// fillStackOut 填充输出栈
func (this *MyQueue) fillStackOut() {
if this.stackOut.Empty() {
for !this.stackIn.Empty() {
val := this.stackIn.Pop()
this.stackOut.Push(val)
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
# JavaScript:
// 使用两个数组的栈方法(push, pop) 实现队列
/**
* Initialize your data structure here.
*/
var MyQueue = function() {
this.stackIn = [];
this.stackOut = [];
};
/**
* Push element x to the back of queue.
* @param {number} x
* @return {void}
*/
MyQueue.prototype.push = function(x) {
this.stackIn.push(x);
};
/**
* Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element.
* @return {number}
*/
MyQueue.prototype.pop = function() {
const size = this.stackOut.length;
if(size) {
return this.stackOut.pop();
}
while(this.stackIn.length) {
this.stackOut.push(this.stackIn.pop());
}
return this.stackOut.pop();
};
/**
* Get the front element.
* @return {number}
*/
MyQueue.prototype.peek = function() {
const x = this.pop();
this.stackOut.push(x);
return x;
};
/**
* Returns whether the queue is empty.
* @return {boolean}
*/
MyQueue.prototype.empty = function() {
return !this.stackIn.length && !this.stackOut.length
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
# TypeScript:
class MyQueue {
private stackIn: number[]
private stackOut: number[]
constructor() {
this.stackIn = [];
this.stackOut = [];
}
push(x: number): void {
this.stackIn.push(x);
}
pop(): number {
if (this.stackOut.length === 0) {
while (this.stackIn.length > 0) {
this.stackOut.push(this.stackIn.pop()!);
}
}
return this.stackOut.pop()!;
}
peek(): number {
let temp: number = this.pop();
this.stackOut.push(temp);
return temp;
}
empty(): boolean {
return this.stackIn.length === 0 && this.stackOut.length === 0;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
# Swift:
class MyQueue {
var stackIn = [Int]()
var stackOut = [Int]()
init() {}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
func push(_ x: Int) {
stackIn.append(x)
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
func pop() -> Int {
if stackOut.isEmpty {
while !stackIn.isEmpty {
stackOut.append(stackIn.popLast()!)
}
}
return stackOut.popLast() ?? -1
}
/** Get the front element. */
func peek() -> Int {
let res = pop()
stackOut.append(res)
return res
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
func empty() -> Bool {
return stackIn.isEmpty && stackOut.isEmpty
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
# C:
/*
1.两个type为int的数组(栈),大小为100
第一个栈stackIn用来存放数据,第二个栈stackOut作为辅助用来输出数据
2.两个指针stackInTop和stackOutTop,分别指向栈顶
*/
typedef struct {
int stackInTop, stackOutTop;
int stackIn[100], stackOut[100];
} MyQueue;
/*
1.开辟一个队列的大小空间
2.将指针stackInTop和stackOutTop初始化为0
3.返回开辟的队列
*/
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue* queue = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
queue->stackInTop = 0;
queue->stackOutTop = 0;
return queue;
}
/*
将元素存入第一个栈中,存入后栈顶指针+1
*/
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
obj->stackIn[(obj->stackInTop)++] = x;
}
/*
1.若输出栈为空且当第一个栈中有元素(stackInTop>0时),将第一个栈中元素复制到第二个栈中(stackOut[stackTop2++] = stackIn[--stackTop1])
2.将栈顶元素保存
3.当stackTop2>0时,将第二个栈中元素复制到第一个栈中(stackIn[stackTop1++] = stackOut[--stackTop2])
*/
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
//优化:复制栈顶指针,减少对内存的访问次数
int stackInTop = obj->stackInTop;
int stackOutTop = obj->stackOutTop;
//若输出栈为空
if(stackOutTop == 0) {
//将第一个栈中元素复制到第二个栈中
while(stackInTop > 0) {
obj->stackOut[stackOutTop++] = obj->stackIn[--stackInTop];
}
}
//将第二个栈中栈顶元素(队列的第一个元素)出栈,并保存
int top = obj->stackOut[--stackOutTop];
//将输出栈中元素放回输入栈中
while(stackOutTop > 0) {
obj->stackIn[stackInTop++] = obj->stackOut[--stackOutTop];
}
//更新栈顶指针
obj->stackInTop = stackInTop;
obj->stackOutTop = stackOutTop;
//返回队列中第一个元素
return top;
}
//返回输入栈中的栈底元素
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
return obj->stackIn[0];
}
//若栈顶指针均为0,则代表队列为空
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
return obj->stackInTop == 0 && obj->stackOutTop == 0;
}
//将栈顶指针置0
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
obj->stackInTop = 0;
obj->stackOutTop = 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
# C#:
public class MyQueue {
Stack<int> inStack;
Stack<int> outStack;
public MyQueue() {
inStack = new Stack<int>();// 负责进栈
outStack = new Stack<int>();// 负责出栈
}
public void Push(int x) {
inStack.Push(x);
}
public int Pop() {
dumpstackIn();
return outStack.Pop();
}
public int Peek() {
dumpstackIn();
return outStack.Peek();
}
public bool Empty() {
return inStack.Count == 0 && outStack.Count == 0;
}
// 处理方法:
// 如果outStack为空,那么将inStack中的元素全部放到outStack中
private void dumpstackIn(){
if (outStack.Count != 0) return;
while(inStack.Count != 0){
outStack.Push(inStack.Pop());
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
# PHP:
// SplStack 类通过使用一个双向链表来提供栈的主要功能。[PHP 5 >= 5.3.0, PHP 7, PHP 8]
// https://www.php.net/manual/zh/class.splstack.php
class MyQueue {
// 双栈模拟队列:In栈存储数据;Out栈辅助处理
private $stackIn;
private $stackOut;
function __construct() {
$this->stackIn = new SplStack();
$this->stackOut = new SplStack();
}
// In: 1 2 3 <= push
function push($x) {
$this->stackIn->push($x);
}
function pop() {
$this->peek();
return $this->stackOut->pop();
}
function peek() {
if($this->stackOut->isEmpty()){
$this->shift();
}
return $this->stackOut->top();
}
function empty() {
return $this->stackOut->isEmpty() && $this->stackIn->isEmpty();
}
// 如果Out栈为空,把In栈数据压入Out栈
// In: 1 2 3 => pop push => 1 2 3 :Out
private function shift(){
while(!$this->stackIn->isEmpty()){
$this->stackOut->push($this->stackIn->pop());
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
# Scala:
class MyQueue() {
import scala.collection.mutable
val stackIn = mutable.Stack[Int]() // 负责出栈
val stackOut = mutable.Stack[Int]() // 负责入栈
// 添加元素
def push(x: Int) {
stackIn.push(x)
}
// 复用代码,如果stackOut为空就把stackIn的所有元素都压入StackOut
def dumpStackIn(): Unit = {
if (!stackOut.isEmpty) return
while (!stackIn.isEmpty) {
stackOut.push(stackIn.pop())
}
}
// 弹出元素
def pop(): Int = {
dumpStackIn()
stackOut.pop()
}
// 获取队头
def peek(): Int = {
dumpStackIn()
val res: Int = stackOut.pop()
stackOut.push(res)
res
}
// 判断是否为空
def empty(): Boolean = {
stackIn.isEmpty && stackOut.isEmpty
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
# Rust:
struct MyQueue {
stack_in: Vec<i32>,
stack_out: Vec<i32>,
}
impl MyQueue {
fn new() -> Self {
MyQueue {
stack_in: Vec::new(),
stack_out: Vec::new(),
}
}
fn push(&mut self, x: i32) {
self.stack_in.push(x);
}
fn pop(&mut self) -> i32 {
if self.stack_out.is_empty(){
while !self.stack_in.is_empty() {
self.stack_out.push(self.stack_in.pop().unwrap());
}
}
self.stack_out.pop().unwrap()
}
fn peek(&mut self) -> i32 {
let res = self.pop();
self.stack_out.push(res);
res
}
fn empty(&self) -> bool {
self.stack_in.is_empty() && self.stack_out.is_empty()
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
← 1. 栈与队列理论基础 3. 用队列实现栈 →

评论
验证登录状态...