# 110.平衡二叉树
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。
本题中,一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1。
示例 1:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]

返回 true 。
示例 2:
给定二叉树 [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4]

返回 false 。
# 算法公开课
《代码随想录》算法视频公开课 (opens new window):后序遍历求高度,高度判断是否平衡 | LeetCode:110.平衡二叉树 (opens new window),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解。
# 题外话
咋眼一看这道题目和104.二叉树的最大深度 (opens new window)很像,其实有很大区别。
这里强调一波概念:
- 二叉树节点的深度:指从根节点到该节点的最长简单路径边的条数。
- 二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数。
但leetcode中强调的深度和高度很明显是按照节点来计算的,如图:
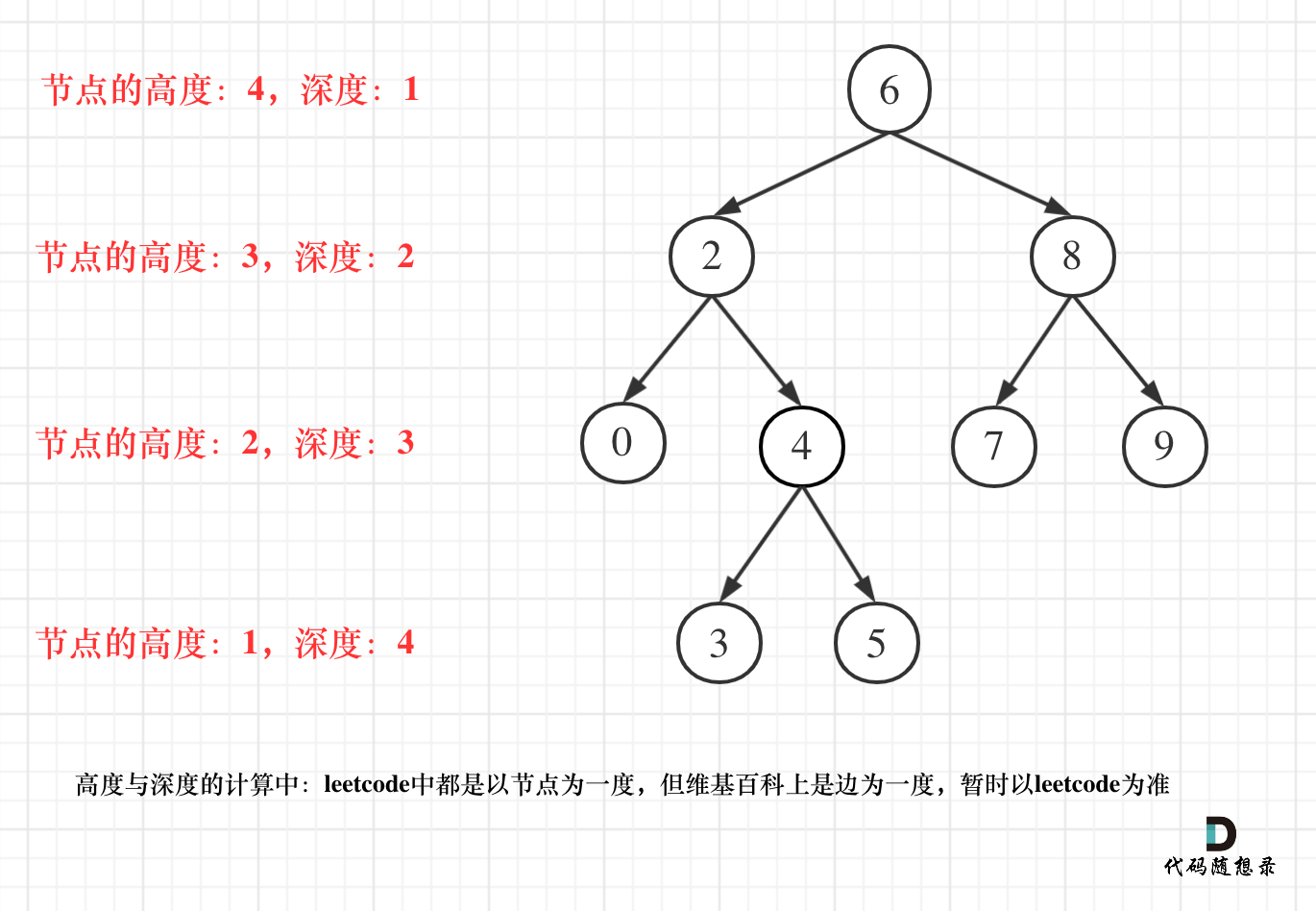
关于根节点的深度究竟是1 还是 0,不同的地方有不一样的标准,leetcode的题目中都是以节点为一度,即根节点深度是1。但维基百科上定义用边为一度,即根节点的深度是0,我们暂时以leetcode为准(毕竟要在这上面刷题)。
因为求深度可以从上到下去查 所以需要前序遍历(中左右),而高度只能从下到上去查,所以只能后序遍历(左右中)
有的同学一定疑惑,为什么104.二叉树的最大深度 (opens new window)中求的是二叉树的最大深度,也用的是后序遍历。
那是因为代码的逻辑其实是求的根节点的高度,而根节点的高度就是这棵树的最大深度,所以才可以使用后序遍历。
在104.二叉树的最大深度 (opens new window)中,如果真正求取二叉树的最大深度,代码应该写成如下:(前序遍历)
class Solution {
public:
int result;
void getDepth(TreeNode* node, int depth) {
result = depth > result ? depth : result; // 中
if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) return ;
if (node->left) { // 左
depth++; // 深度+1
getDepth(node->left, depth);
depth--; // 回溯,深度-1
}
if (node->right) { // 右
depth++; // 深度+1
getDepth(node->right, depth);
depth--; // 回溯,深度-1
}
return ;
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
result = 0;
if (root == NULL) return result;
getDepth(root, 1);
return result;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
可以看出使用了前序(中左右)的遍历顺序,这才是真正求深度的逻辑!
注意以上代码是为了把细节体现出来,简化一下代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int result;
void getDepth(TreeNode* node, int depth) {
result = depth > result ? depth : result; // 中
if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) return ;
if (node->left) { // 左
getDepth(node->left, depth + 1);
}
if (node->right) { // 右
getDepth(node->right, depth + 1);
}
return ;
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
result = 0;
if (root == 0) return result;
getDepth(root, 1);
return result;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# 本题思路
# 递归
此时大家应该明白了既然要求比较高度,必然是要后序遍历。
递归三步曲分析:
- 明确递归函数的参数和返回值
参数:当前传入节点。 返回值:以当前传入节点为根节点的树的高度。
那么如何标记左右子树是否差值大于1呢?
如果当前传入节点为根节点的二叉树已经不是二叉平衡树了,还返回高度的话就没有意义了。
所以如果已经不是二叉平衡树了,可以返回-1 来标记已经不符合平衡树的规则了。
代码如下:
// -1 表示已经不是平衡二叉树了,否则返回值是以该节点为根节点树的高度
int getHeight(TreeNode* node)
2
- 明确终止条件
递归的过程中依然是遇到空节点了为终止,返回0,表示当前节点为根节点的树高度为0
代码如下:
if (node == NULL) {
return 0;
}
2
3
- 明确单层递归的逻辑
如何判断以当前传入节点为根节点的二叉树是否是平衡二叉树呢?当然是其左子树高度和其右子树高度的差值。
分别求出其左右子树的高度,然后如果差值小于等于1,则返回当前二叉树的高度,否则返回-1,表示已经不是二叉平衡树了。
代码如下:
int leftHeight = getHeight(node->left); // 左
if (leftHeight == -1) return -1;
int rightHeight = getHeight(node->right); // 右
if (rightHeight == -1) return -1;
int result;
if (abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1) { // 中
result = -1;
} else {
result = 1 + max(leftHeight, rightHeight); // 以当前节点为根节点的树的最大高度
}
return result;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
代码精简之后如下:
int leftHeight = getHeight(node->left);
if (leftHeight == -1) return -1;
int rightHeight = getHeight(node->right);
if (rightHeight == -1) return -1;
return abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1 ? -1 : 1 + max(leftHeight, rightHeight);
2
3
4
5
此时递归的函数就已经写出来了,这个递归的函数传入节点指针,返回以该节点为根节点的二叉树的高度,如果不是二叉平衡树,则返回-1。
getHeight整体代码如下:
int getHeight(TreeNode* node) {
if (node == NULL) {
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = getHeight(node->left);
if (leftHeight == -1) return -1;
int rightHeight = getHeight(node->right);
if (rightHeight == -1) return -1;
return abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1 ? -1 : 1 + max(leftHeight, rightHeight);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
最后本题整体递归代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
// 返回以该节点为根节点的二叉树的高度,如果不是平衡二叉树了则返回-1
int getHeight(TreeNode* node) {
if (node == NULL) {
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = getHeight(node->left);
if (leftHeight == -1) return -1;
int rightHeight = getHeight(node->right);
if (rightHeight == -1) return -1;
return abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1 ? -1 : 1 + max(leftHeight, rightHeight);
}
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
return getHeight(root) == -1 ? false : true;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 迭代
在104.二叉树的最大深度 (opens new window)中我们可以使用层序遍历来求深度,但是就不能直接用层序遍历来求高度了,这就体现出求高度和求深度的不同。
本题的迭代方式可以先定义一个函数,专门用来求高度。
这个函数通过栈模拟的后序遍历找每一个节点的高度(其实是通过求传入节点为根节点的最大深度来求的高度)
代码如下:
// cur节点的最大深度,就是cur的高度
int getDepth(TreeNode* cur) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
if (cur != NULL) st.push(cur);
int depth = 0; // 记录深度
int result = 0;
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top();
if (node != NULL) {
st.pop();
st.push(node); // 中
st.push(NULL);
depth++;
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 右
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 左
} else {
st.pop();
node = st.top();
st.pop();
depth--;
}
result = result > depth ? result : depth;
}
return result;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
然后再用栈来模拟后序遍历,遍历每一个节点的时候,再去判断左右孩子的高度是否符合,代码如下:
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
if (root == NULL) return true;
st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top(); // 中
st.pop();
if (abs(getDepth(node->left) - getDepth(node->right)) > 1) { // 判断左右孩子高度是否符合
return false;
}
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 右(空节点不入栈)
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 左(空节点不入栈)
}
return true;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
整体代码如下:
class Solution {
private:
int getDepth(TreeNode* cur) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
if (cur != NULL) st.push(cur);
int depth = 0; // 记录深度
int result = 0;
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top();
if (node != NULL) {
st.pop();
st.push(node); // 中
st.push(NULL);
depth++;
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 右
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 左
} else {
st.pop();
node = st.top();
st.pop();
depth--;
}
result = result > depth ? result : depth;
}
return result;
}
public:
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
if (root == NULL) return true;
st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top(); // 中
st.pop();
if (abs(getDepth(node->left) - getDepth(node->right)) > 1) {
return false;
}
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 右(空节点不入栈)
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 左(空节点不入栈)
}
return true;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
当然此题用迭代法,其实效率很低,因为没有很好的模拟回溯的过程,所以迭代法有很多重复的计算。
虽然理论上所有的递归都可以用迭代来实现,但是有的场景难度可能比较大。
例如:都知道回溯法其实就是递归,但是很少人用迭代的方式去实现回溯算法!
因为对于回溯算法已经是非常复杂的递归了,如果再用迭代的话,就是自己给自己找麻烦,效率也并不一定高。
# 总结
通过本题可以了解求二叉树深度 和 二叉树高度的差异,求深度适合用前序遍历,而求高度适合用后序遍历。
本题迭代法其实有点复杂,大家可以有一个思路,也不一定说非要写出来。
但是递归方式是一定要掌握的!
# 其他语言版本
# Java:
class Solution {
/**
* 递归法
*/
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
return getHeight(root) != -1;
}
private int getHeight(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = getHeight(root.left);
if (leftHeight == -1) {
return -1;
}
int rightHeight = getHeight(root.right);
if (rightHeight == -1) {
return -1;
}
// 左右子树高度差大于1,return -1表示已经不是平衡树了
if (Math.abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1) {
return -1;
}
return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
}
}
class Solution {
/**
* 迭代法,效率较低,计算高度时会重复遍历
* 时间复杂度:O(n^2)
*/
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode pre = null;
while (root!= null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
TreeNode inNode = stack.peek();
// 右结点为null或已经遍历过
if (inNode.right == null || inNode.right == pre) {
// 比较左右子树的高度差,输出
if (Math.abs(getHeight(inNode.left) - getHeight(inNode.right)) > 1) {
return false;
}
stack.pop();
pre = inNode;
root = null;// 当前结点下,没有要遍历的结点了
} else {
root = inNode.right;// 右结点还没遍历,遍历右结点
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* 层序遍历,求结点的高度
*/
public int getHeight(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
Deque<TreeNode> deque = new LinkedList<>();
deque.offer(root);
int depth = 0;
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
int size = deque.size();
depth++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode poll = deque.poll();
if (poll.left != null) {
deque.offer(poll.left);
}
if (poll.right != null) {
deque.offer(poll.right);
}
}
}
return depth;
}
}
class Solution {
/**
* 优化迭代法,针对暴力迭代法的getHeight方法做优化,利用TreeNode.val来保存当前结点的高度,这样就不会有重复遍历
* 获取高度算法时间复杂度可以降到O(1),总的时间复杂度降为O(n)。
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
*/
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode pre = null;
while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
TreeNode inNode = stack.peek();
// 右结点为null或已经遍历过
if (inNode.right == null || inNode.right == pre) {
// 输出
if (Math.abs(getHeight(inNode.left) - getHeight(inNode.right)) > 1) {
return false;
}
stack.pop();
pre = inNode;
root = null;// 当前结点下,没有要遍历的结点了
} else {
root = inNode.right;// 右结点还没遍历,遍历右结点
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* 求结点的高度
*/
public int getHeight(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = root.left != null ? root.left.val : 0;
int rightHeight = root.right != null ? root.right.val : 0;
int height = Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
root.val = height;// 用TreeNode.val来保存当前结点的高度
return height;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
# Python:
递归法:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def isBalanced(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
if self.get_height(root) != -1:
return True
else:
return False
def get_height(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
# Base Case
if not root:
return 0
# 左
if (left_height := self.get_height(root.left)) == -1:
return -1
# 右
if (right_height := self.get_height(root.right)) == -1:
return -1
# 中
if abs(left_height - right_height) > 1:
return -1
else:
return 1 + max(left_height, right_height)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
递归法精简版:
class Solution:
def isBalanced(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
return self.get_hight(root) != -1
def get_hight(self, node):
if not node:
return 0
left = self.get_hight(node.left)
right = self.get_hight(node.right)
if left == -1 or right == -1 or abs(left - right) > 1:
return -1
return max(left, right) + 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
迭代法:
class Solution:
def getDepth(self, cur):
st = []
if cur is not None:
st.append(cur)
depth = 0
result = 0
while st:
node = st[-1]
if node is not None:
st.pop()
st.append(node) # 中
st.append(None)
depth += 1
if node.right:
st.append(node.right) # 右
if node.left:
st.append(node.left) # 左
else:
node = st.pop()
st.pop()
depth -= 1
result = max(result, depth)
return result
def isBalanced(self, root):
st = []
if root is None:
return True
st.append(root)
while st:
node = st.pop() # 中
if abs(self.getDepth(node.left) - self.getDepth(node.right)) > 1:
return False
if node.right:
st.append(node.right) # 右(空节点不入栈)
if node.left:
st.append(node.left) # 左(空节点不入栈)
return True
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
迭代法精简版:
class Solution:
def isBalanced(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
if not root:
return True
height_map = {}
stack = [root]
while stack:
node = stack.pop()
if node:
stack.append(node) # 中
stack.append(None)
# 采用数组进行迭代,先将右节点加入,保证左节点能够先出栈
if node.right: # 右
stack.append(node.right)
if node.left: # 左
stack.append(node.left)
else:
real_node = stack.pop()
left, right = height_map.get(real_node.left, 0), height_map.get(real_node.right, 0)
if abs(left - right) > 1:
return False
height_map[real_node] = 1 + max(left, right)
return True
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# Go:
递归法
func isBalanced(root *TreeNode) bool {
h := getHeight(root)
if h == -1 {
return false
}
return true
}
// 返回以该节点为根节点的二叉树的高度,如果不是平衡二叉树了则返回-1
func getHeight(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
l, r := getHeight(root.Left), getHeight(root.Right)
if l == -1 || r == -1 {
return -1
}
if l - r > 1 || r - l > 1 {
return -1
}
return max(l, r) + 1
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
迭代法
func isBalanced(root *TreeNode) bool {
st := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
if root == nil {
return true
}
st = append(st, root)
for len(st) > 0 {
node := st[len(st)-1]
st = st[:len(st)-1]
if math.Abs(float64(getDepth(node.Left)) - float64(getDepth(node.Right))) > 1 {
return false
}
if node.Right != nil {
st = append(st, node.Right)
}
if node.Left != nil {
st = append(st, node.Left)
}
}
return true
}
func getDepth(cur *TreeNode) int {
st := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
if cur != nil {
st = append(st, cur)
}
depth := 0
result := 0
for len(st) > 0 {
node := st[len(st)-1]
if node != nil {
st = st[:len(st)-1]
st = append(st, node, nil)
depth++
if node.Right != nil {
st = append(st, node.Right)
}
if node.Left != nil {
st = append(st, node.Left)
}
} else {
st = st[:len(st)-1]
node = st[len(st)-1]
st = st[:len(st)-1]
depth--
}
if result < depth {
result = depth
}
}
return result
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
# JavaScript:
递归法:
var isBalanced = function(root) {
//还是用递归三部曲 + 后序遍历 左右中 当前左子树右子树高度相差大于1就返回-1
// 1. 确定递归函数参数以及返回值
const getDepth = function(node) {
// 2. 确定递归函数终止条件
if(node === null) return 0;
// 3. 确定单层递归逻辑
let leftDepth = getDepth(node.left); //左子树高度
// 当判定左子树不为平衡二叉树时,即可直接返回-1
if(leftDepth === -1) return -1;
let rightDepth = getDepth(node.right); //右子树高度
// 当判定右子树不为平衡二叉树时,即可直接返回-1
if(rightDepth === -1) return -1;
if(Math.abs(leftDepth - rightDepth) > 1) {
return -1;
} else {
return 1 + Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth);
}
}
return !(getDepth(root) === -1);
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
迭代法:
// 获取当前节点的高度
var getHeight = function (curNode) {
let queue = [];
if (curNode !== null) queue.push(curNode); // 压入当前元素
let depth = 0, res = 0;
while (queue.length) {
let node = queue[queue.length - 1]; // 取出栈顶
if (node !== null) {
queue.pop();
queue.push(node); // 中
queue.push(null);
depth++;
node.right && queue.push(node.right); // 右
node.left && queue.push(node.left); // 左
} else {
queue.pop();
node = queue[queue.length - 1];
queue.pop();
depth--;
}
res = res > depth ? res : depth;
}
return res;
}
var isBalanced = function (root) {
if (root === null) return true;
let queue = [root];
while (queue.length) {
let node = queue[queue.length - 1]; // 取出栈顶
queue.pop();
if (Math.abs(getHeight(node.left) - getHeight(node.right)) > 1) {
return false;
}
node.right && queue.push(node.right);
node.left && queue.push(node.left);
}
return true;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
# TypeScript:
// 递归法
function isBalanced(root: TreeNode | null): boolean {
function getDepth(root: TreeNode | null): number {
if (root === null) return 0;
let leftDepth: number = getDepth(root.left);
if (leftDepth === -1) return -1;
let rightDepth: number = getDepth(root.right);
if (rightDepth === -1) return -1;
if (Math.abs(leftDepth - rightDepth) > 1) return -1;
return 1 + Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth);
}
return getDepth(root) !== -1;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# C:
递归法:
int getDepth(struct TreeNode* node) {
//如果结点不存在,返回0
if(!node)
return 0;
//求出右子树深度
int rightDepth = getDepth(node->right);
//求出左子树深度
int leftDepth = getDepth(node->left);
//返回左右子树中的较大值+1
return rightDepth > leftDepth ? rightDepth + 1 : leftDepth + 1;
}
bool isBalanced(struct TreeNode* root) {
//递归结束条件为:传入结点为NULL,返回True
if(!root)
return 1;
//求出左右子树的深度
int leftDepth = getDepth(root->left);
int rightDepth = getDepth(root->right);
int diff;
//若左右子树绝对值差距大于1,返回False
if((diff = leftDepth - rightDepth) > 1 || diff < -1)
return 0;
//检查左右子树是否为平衡二叉树
return isBalanced(root->right) && isBalanced(root->left);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
迭代法:
//计算结点深度
int getDepth(struct TreeNode* node) {
//开辟栈空间
struct TreeNode** stack = (struct TreeNode**)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode*) * 10000);
int stackTop = 0;
//若传入结点存在,将其入栈。若不存在,函数直接返回0
if(node)
stack[stackTop++] = node;
int result = 0;
int depth = 0;
//当栈中有元素时,进行迭代遍历
while(stackTop) {
//取出栈顶元素
struct TreeNode* tempNode = stack[--stackTop];
//若栈顶元素非NULL,则将深度+1
if(tempNode) {
depth++;
//将栈顶元素再次入栈,添加NULL表示此结点已被遍历
stack[stackTop++] = tempNode;
stack[stackTop++] = NULL;
//若栈顶元素有左右孩子,则将孩子结点入栈
if(tempNode->left)
stack[stackTop++] = tempNode->left;
if(tempNode->right)
stack[stackTop++] = tempNode->right;
//更新结果
result = result > depth ? result : depth;
}
else {
//若为NULL,则代表当前结点已被遍历,深度-1
tempNode = stack[--stackTop];
depth--;
}
}
return result;
}
bool isBalanced(struct TreeNode* root){
//开辟栈空间
struct TreeNode** stack = (struct TreeNode**)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode*) * 10000);
int stackTop = 0;
//若根节点不存在,返回True
if(!root)
return 1;
//将根节点入栈
stack[stackTop++] = root;
//当栈中有元素时,进行遍历
while(stackTop) {
//将栈顶元素出栈
struct TreeNode* node = stack[--stackTop];
//计算左右子树的深度
int diff = getDepth(node->right) - getDepth(node->left);
//若深度的绝对值大于1,返回False
if(diff > 1 || diff < -1)
return 0;
//如果栈顶结点有左右结点,将左右结点入栈
if(node->left)
stack[stackTop++] = node->left;
if(node->right)
stack[stackTop++] = node->right;
}
//若二叉树遍历结束后没有返回False,则返回True
return 1;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
# Swift:
递归
func isBalanced(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Bool {
// -1 已经不是平衡二叉树
return getHeight(root) == -1 ? false : true
}
func getHeight(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Int {
guard let root = root else {
return 0
}
let leftHeight = getHeight(root.left)
if leftHeight == -1 {
return -1
}
let rightHeight = getHeight(root.right)
if rightHeight == -1 {
return -1
}
if abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1 {
return -1
} else {
return 1 + max(leftHeight, rightHeight)
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# Rust:
递归
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::rc::Rc;
impl Solution {
pub fn is_balanced(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> bool {
Self::get_depth(root) != -1
}
pub fn get_depth(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 {
if root.is_none() {
return 0;
}
let right = Self::get_depth(root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow().left.clone());
let left = Self::get_depth(root.unwrap().borrow().right.clone());
if right == -1 {
return -1;
}
if left == -1 {
return -1;
}
if (right - left).abs() > 1 {
return -1;
}
1 + right.max(left)
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# C#
public bool IsBalanced(TreeNode root)
{
return GetHeight(root) == -1 ? false : true;
}
public int GetHeight(TreeNode root)
{
if (root == null) return 0;
int left = GetHeight(root.left);
if (left == -1) return -1;
int right = GetHeight(root.right);
if (right == -1) return -1;
int res;
if (Math.Abs(left - right) > 1)
{
res = -1;
}
else
{
res = 1 + Math.Max(left, right);
}
return res;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
