- 做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目) (opens new window)
- 刷算法(两个月高强度学算法) (opens new window)
- 背八股(40天挑战高频面试题) (opens new window)
# 51. N皇后
n 皇后问题 研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,并且使皇后彼此之间不能相互攻击。
给你一个整数 n ,返回所有不同的 n 皇后问题 的解决方案。
每一种解法包含一个不同的 n 皇后问题 的棋子放置方案,该方案中 'Q' 和 '.' 分别代表了皇后和空位。
示例 1:
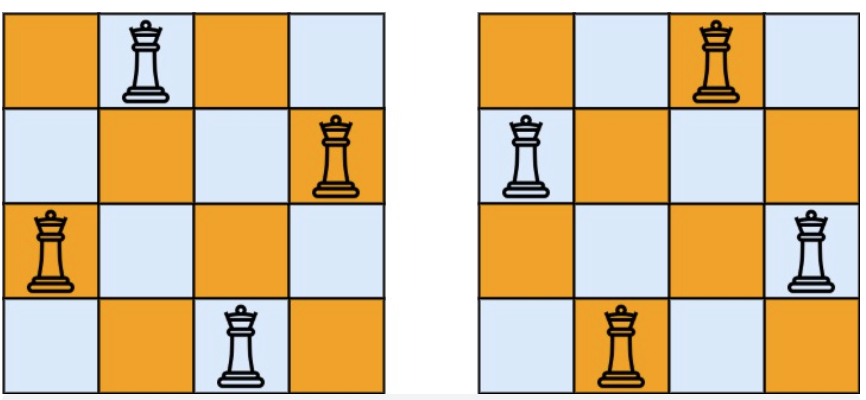
- 输入:n = 4
- 输出:[[".Q..","...Q","Q...","..Q."],["..Q.","Q...","...Q",".Q.."]]
- 解释:如上图所示,4 皇后问题存在两个不同的解法。
示例 2:
- 输入:n = 1
- 输出:[["Q"]]
# 算法公开课
《代码随想录》算法视频公开课 (opens new window):这就是传说中的N皇后? 回溯算法安排!| LeetCode:51.N皇后 (opens new window),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解。
# 思路
都知道n皇后问题是回溯算法解决的经典问题,但是用回溯解决多了组合、切割、子集、排列问题之后,遇到这种二维矩阵还会有点不知所措。
首先来看一下皇后们的约束条件:
- 不能同行
- 不能同列
- 不能同斜线
确定完约束条件,来看看究竟要怎么去搜索皇后们的位置,其实搜索皇后的位置,可以抽象为一棵树。
下面我用一个 3 * 3 的棋盘,将搜索过程抽象为一棵树,如图:
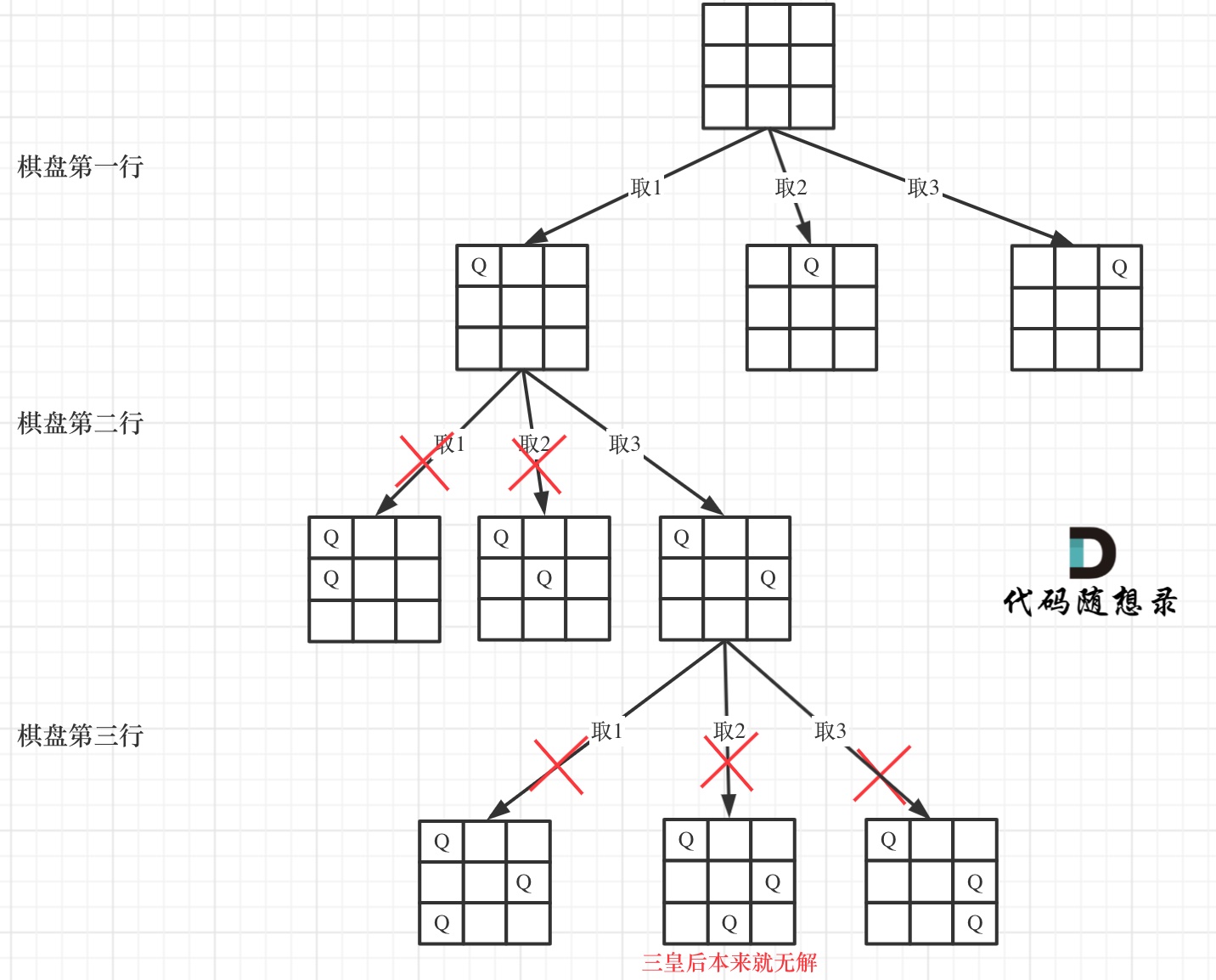
从图中,可以看出,二维矩阵中矩阵的高就是这棵树的高度,矩阵的宽就是树形结构中每一个节点的宽度。
那么我们用皇后们的约束条件,来回溯搜索这棵树,只要搜索到了树的叶子节点,说明就找到了皇后们的合理位置了。
# 回溯三部曲
按照我总结的如下回溯模板,我们来依次分析:
void backtracking(参数) {
if (终止条件) {
存放结果;
return;
}
for (选择:本层集合中元素(树中节点孩子的数量就是集合的大小)) {
处理节点;
backtracking(路径,选择列表); // 递归
回溯,撤销处理结果
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
- 递归函数参数
我依然是定义全局变量二维数组result来记录最终结果。
参数n是棋盘的大小,然后用row来记录当前遍历到棋盘的第几层了。
代码如下:
vector<vector<string>> result;
void backtracking(int n, int row, vector<string>& chessboard) {
2
- 递归终止条件
在如下树形结构中:
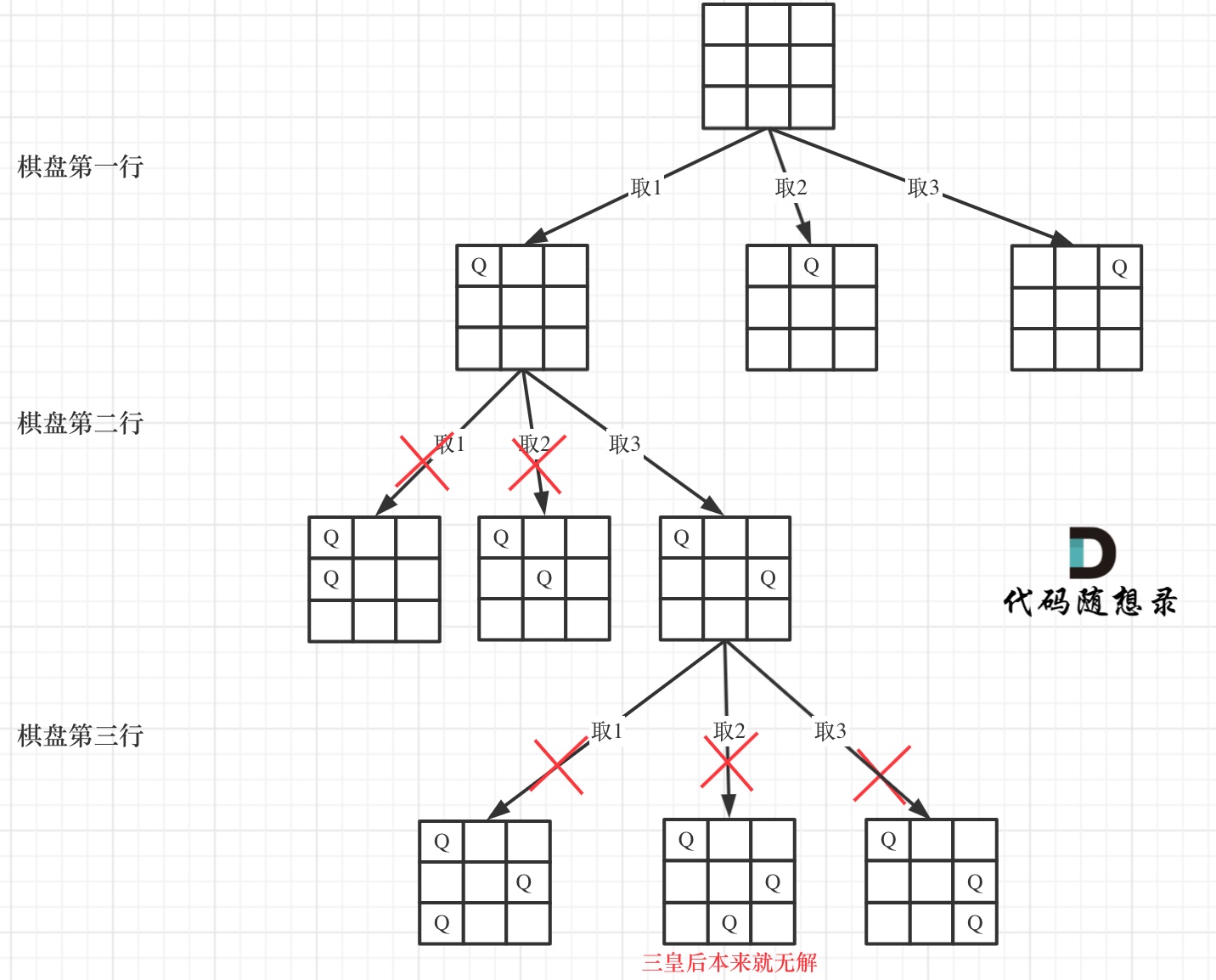
可以看出,当递归到棋盘最底层(也就是叶子节点)的时候,就可以收集结果并返回了。
代码如下:
if (row == n) {
result.push_back(chessboard);
return;
}
2
3
4
- 单层搜索的逻辑
递归深度就是row控制棋盘的行,每一层里for循环的col控制棋盘的列,一行一列,确定了放置皇后的位置。
每次都是要从新的一行的起始位置开始搜,所以都是从0开始。
代码如下:
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
if (isValid(row, col, chessboard, n)) { // 验证合法就可以放
chessboard[row][col] = 'Q'; // 放置皇后
backtracking(n, row + 1, chessboard);
chessboard[row][col] = '.'; // 回溯,撤销皇后
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
- 验证棋盘是否合法
按照如下标准去重:
- 不能同行
- 不能同列
- 不能同斜线 (45度和135度角)
代码如下:
bool isValid(int row, int col, vector<string>& chessboard, int n) {
// 检查列
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) { // 这是一个剪枝
if (chessboard[i][col] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
// 检查 45度角是否有皇后
for (int i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i >=0 && j >= 0; i--, j--) {
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
// 检查 135度角是否有皇后
for(int i = row - 1, j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < n; i--, j++) {
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
在这份代码中,细心的同学可以发现为什么没有在同行进行检查呢?
因为在单层搜索的过程中,每一层递归,只会选for循环(也就是同一行)里的一个元素,所以不用去重了。
那么按照这个模板不难写出如下C++代码:
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<string>> result;
// n 为输入的棋盘大小
// row 是当前递归到棋盘的第几行了
void backtracking(int n, int row, vector<string>& chessboard) {
if (row == n) {
result.push_back(chessboard);
return;
}
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
if (isValid(row, col, chessboard, n)) { // 验证合法就可以放
chessboard[row][col] = 'Q'; // 放置皇后
backtracking(n, row + 1, chessboard);
chessboard[row][col] = '.'; // 回溯,撤销皇后
}
}
}
bool isValid(int row, int col, vector<string>& chessboard, int n) {
// 检查列
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) { // 这是一个剪枝
if (chessboard[i][col] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
// 检查 45度角是否有皇后
for (int i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i >=0 && j >= 0; i--, j--) {
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
// 检查 135度角是否有皇后
for(int i = row - 1, j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < n; i--, j++) {
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public:
vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int n) {
result.clear();
std::vector<std::string> chessboard(n, std::string(n, '.'));
backtracking(n, 0, chessboard);
return result;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
- 时间复杂度: O(n!)
- 空间复杂度: O(n)
可以看出,除了验证棋盘合法性的代码,省下来部分就是按照回溯法模板来的。
# 总结
本题是我们解决棋盘问题的第一道题目。
如果从来没有接触过N皇后问题的同学看着这样的题会感觉无从下手,可能知道要用回溯法,但也不知道该怎么去搜。
这里我明确给出了棋盘的宽度就是for循环的长度,递归的深度就是棋盘的高度,这样就可以套进回溯法的模板里了。
大家可以在仔细体会体会!
# 其他语言补充
# Java
class Solution {
List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
char[][] chessboard = new char[n][n];
for (char[] c : chessboard) {
Arrays.fill(c, '.');
}
backTrack(n, 0, chessboard);
return res;
}
public void backTrack(int n, int row, char[][] chessboard) {
if (row == n) {
res.add(Array2List(chessboard));
return;
}
for (int col = 0;col < n; ++col) {
if (isValid (row, col, n, chessboard)) {
chessboard[row][col] = 'Q';
backTrack(n, row+1, chessboard);
chessboard[row][col] = '.';
}
}
}
public List Array2List(char[][] chessboard) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (char[] c : chessboard) {
list.add(String.copyValueOf(c));
}
return list;
}
public boolean isValid(int row, int col, int n, char[][] chessboard) {
// 检查列
for (int i=0; i<row; ++i) { // 相当于剪枝
if (chessboard[i][col] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
// 检查45度对角线
for (int i=row-1, j=col-1; i>=0 && j>=0; i--, j--) {
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
// 检查135度对角线
for (int i=row-1, j=col+1; i>=0 && j<=n-1; i--, j++) {
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
// 方法2:使用boolean数组表示已经占用的直(斜)线
class Solution {
List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[] usedCol, usedDiag45, usedDiag135; // boolean数组中的每个元素代表一条直(斜)线
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
usedCol = new boolean[n]; // 列方向的直线条数为 n
usedDiag45 = new boolean[2 * n - 1]; // 45°方向的斜线条数为 2 * n - 1
usedDiag135 = new boolean[2 * n - 1]; // 135°方向的斜线条数为 2 * n - 1
//用于收集结果, 元素的index表示棋盘的row,元素的value代表棋盘的column
int[] board = new int[n];
backTracking(board, n, 0);
return res;
}
private void backTracking(int[] board, int n, int row) {
if (row == n) {
//收集结果
List<String> temp = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i : board) {
char[] str = new char[n];
Arrays.fill(str, '.');
str[i] = 'Q';
temp.add(new String(str));
}
res.add(temp);
return;
}
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
if (usedCol[col] | usedDiag45[row + col] | usedDiag135[row - col + n - 1]) {
continue;
}
board[row] = col;
// 标记该列出现过
usedCol[col] = true;
// 同一45°斜线上元素的row + col为定值, 且各不相同
usedDiag45[row + col] = true;
// 同一135°斜线上元素row - col为定值, 且各不相同
// row - col 值有正有负, 加 n - 1 是为了对齐零点
usedDiag135[row - col + n - 1] = true;
// 递归
backTracking(board, n, row + 1);
usedCol[col] = false;
usedDiag45[row + col] = false;
usedDiag135[row - col + n - 1] = false;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
# Python
class Solution:
def solveNQueens(self, n: int) -> List[List[str]]:
result = [] # 存储最终结果的二维字符串数组
chessboard = ['.' * n for _ in range(n)] # 初始化棋盘
self.backtracking(n, 0, chessboard, result) # 回溯求解
return [[''.join(row) for row in solution] for solution in result] # 返回结果集
def backtracking(self, n: int, row: int, chessboard: List[str], result: List[List[str]]) -> None:
if row == n:
result.append(chessboard[:]) # 棋盘填满,将当前解加入结果集
return
for col in range(n):
if self.isValid(row, col, chessboard):
chessboard[row] = chessboard[row][:col] + 'Q' + chessboard[row][col+1:] # 放置皇后
self.backtracking(n, row + 1, chessboard, result) # 递归到下一行
chessboard[row] = chessboard[row][:col] + '.' + chessboard[row][col+1:] # 回溯,撤销当前位置的皇后
def isValid(self, row: int, col: int, chessboard: List[str]) -> bool:
# 检查列
for i in range(row):
if chessboard[i][col] == 'Q':
return False # 当前列已经存在皇后,不合法
# 检查 45 度角是否有皇后
i, j = row - 1, col - 1
while i >= 0 and j >= 0:
if chessboard[i][j] == 'Q':
return False # 左上方向已经存在皇后,不合法
i -= 1
j -= 1
# 检查 135 度角是否有皇后
i, j = row - 1, col + 1
while i >= 0 and j < len(chessboard):
if chessboard[i][j] == 'Q':
return False # 右上方向已经存在皇后,不合法
i -= 1
j += 1
return True # 当前位置合法
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
# Go
func solveNQueens(n int) [][]string {
var res [][]string
chessboard := make([][]string, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
chessboard[i] = make([]string, n)
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
chessboard[i][j] = "."
}
}
var backtrack func(int)
backtrack = func(row int) {
if row == n {
temp := make([]string, n)
for i, rowStr := range chessboard {
temp[i] = strings.Join(rowStr, "")
}
res = append(res, temp)
return
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
if isValid(n, row, i, chessboard) {
chessboard[row][i] = "Q"
backtrack(row + 1)
chessboard[row][i] = "."
}
}
}
backtrack(0)
return res
}
func isValid(n, row, col int, chessboard [][]string) bool {
for i := 0; i < row; i++ {
if chessboard[i][col] == "Q" {
return false
}
}
for i, j := row-1, col-1; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i, j = i-1, j-1 {
if chessboard[i][j] == "Q" {
return false
}
}
for i, j := row-1, col+1; i >= 0 && j < n; i, j = i-1, j+1 {
if chessboard[i][j] == "Q" {
return false
}
}
return true
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
# JavaScript
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {string[][]}
*/
var solveNQueens = function (n) {
const ans = [];
const path = [];
const matrix = new Array(n).fill(0).map(() => new Array(n).fill("."));
// 判断是否能相互攻击
const canAttack = (matrix, row, col) => {
let i;
let j;
// 判断正上方和正下方是否有皇后
for (i = 0, j = col; i < n; i++) {
if (matrix[i][j] === "Q") {
return true;
}
}
// 判断正左边和正右边是否有皇后
for (i = row, j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (matrix[i][j] === "Q") {
return true;
}
}
// 判断左上方是否有皇后
for (i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--) {
if (matrix[i][j] === "Q") {
return true;
}
}
// 判断右上方是否有皇后
for (i = row - 1, j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < n; i--, j++) {
if (matrix[i][j] === "Q") {
return true;
}
}
return false;
};
const backtrack = (matrix, row, col) => {
if (path.length === matrix.length) {
ans.push(path.slice());
return;
}
for (let i = row; i < matrix.length; i++) {
for (let j = col; j < matrix.length; j++) {
// 当前位置会导致互相攻击 继续下一轮搜索
if (canAttack(matrix, i, j)) {
continue;
}
matrix[i][j] = "Q";
path.push(matrix[i].join(""));
// 另起一行搜索 同一行只能有一个皇后
backtrack(matrix, i + 1, 0);
matrix[i][j] = ".";
path.pop();
}
}
};
backtrack(matrix, 0, 0);
return ans;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
# TypeScript
function solveNQueens(n: number): string[][] {
const board: string[][] = new Array(n).fill(0).map(_ => new Array(n).fill('.'));
const resArr: string[][] = [];
backTracking(n, 0, board);
return resArr;
function backTracking(n: number, rowNum: number, board: string[][]): void {
if (rowNum === n) {
resArr.push(transformBoard(board));
return;
}
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (isValid(i, rowNum, board) === true) {
board[rowNum][i] = 'Q';
backTracking(n, rowNum + 1, board);
board[rowNum][i] = '.';
}
}
}
};
function isValid(col: number, row: number, board: string[][]): boolean {
const n: number = board.length;
if (col < 0 || col >= n || row < 0 || row >= n) return false;
// 检查列
for (let row of board) {
if (row[col] === 'Q') return false;
}
// 检查45度方向
let x: number = col,
y: number = row;
while (y >= 0 && x < n) {
if (board[y--][x++] === 'Q') return false;
}
// 检查135度方向
x = col;
y = row;
while (x >= 0 && y >= 0) {
if (board[y--][x--] === 'Q') return false;
}
return true;
}
function transformBoard(board: string[][]): string[] {
const resArr = [];
for (let row of board) {
resArr.push(row.join(''));
}
return resArr;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
# Swift
func solveNQueens(_ n: Int) -> [[String]] {
var result = [[String]]()
// 棋盘,使用Character的二维数组,以便于更新元素
var chessboard = [[Character]](repeating: [Character](repeating: ".", count: n), count: n)
// 检查棋盘是否符合N皇后
func isVaild(row: Int, col: Int) -> Bool {
// 检查列
for i in 0 ..< row {
if chessboard[i][col] == "Q" { return false }
}
var i, j: Int
// 检查45度
i = row - 1
j = col - 1
while i >= 0, j >= 0 {
if chessboard[i][j] == "Q" { return false }
i -= 1
j -= 1
}
// 检查135度
i = row - 1
j = col + 1
while i >= 0, j < n {
if chessboard[i][j] == "Q" { return false }
i -= 1
j += 1
}
return true
}
func backtracking(row: Int) {
if row == n {
result.append(chessboard.map { String($0) })
}
for col in 0 ..< n {
guard isVaild(row: row, col: col) else { continue }
chessboard[row][col] = "Q" // 放置皇后
backtracking(row: row + 1)
chessboard[row][col] = "." // 回溯
}
}
backtracking(row: 0)
return result
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
# Rust
impl Solution {
fn is_valid(row: usize, col: usize, chessboard: &mut Vec<Vec<char>>, n: usize) -> bool {
let mut i = 0 as usize;
while i < row {
if chessboard[i][col] == 'Q' { return false; }
i += 1;
}
let (mut i, mut j) = (row as i32 - 1, col as i32 - 1);
while i >= 0 && j >= 0 {
if chessboard[i as usize][j as usize] == 'Q' { return false; }
i -= 1;
j -= 1;
}
let (mut i, mut j) = (row as i32 - 1, col as i32 + 1);
while i >= 0 && j < n as i32 {
if chessboard[i as usize][j as usize] == 'Q' { return false; }
i -= 1;
j += 1;
}
return true;
}
fn backtracking(result: &mut Vec<Vec<String>>, n: usize, row: usize, chessboard: &mut Vec<Vec<char>>) {
if row == n {
let mut chessboard_clone: Vec<String> = Vec::new();
for i in chessboard {
chessboard_clone.push(i.iter().collect::<String>());
}
result.push(chessboard_clone);
return;
}
for col in 0..n {
if Self::is_valid(row, col, chessboard, n) {
chessboard[row][col] = 'Q';
Self::backtracking(result, n, row + 1, chessboard);
chessboard[row][col] = '.';
}
}
}
pub fn solve_n_queens(n: i32) -> Vec<Vec<String>> {
let mut result: Vec<Vec<String>> = Vec::new();
let mut chessboard: Vec<Vec<char>> = vec![vec!['.'; n as usize]; n as usize];
Self::backtracking(&mut result, n as usize, 0, &mut chessboard);
result
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
# C
char ***ans;
char **path;
int ansTop, pathTop;
//将path中元素复制到ans中
void copyPath(int n) {
char **tempPath = (char**)malloc(sizeof(char*) * pathTop);
int i;
for(i = 0; i < pathTop; ++i) {
tempPath[i] = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * n + 1);
int j;
for(j = 0; j < n; ++j)
tempPath[i][j] = path[i][j];
tempPath[i][j] = '\0';
}
ans[ansTop++] = tempPath;
}
//判断当前位置是否有效(是否不被其它皇后影响)
int isValid(int x, int y, int n) {
int i, j;
//检查同一行以及同一列是否有效
for(i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if(path[y][i] == 'Q' || path[i][x] == 'Q')
return 0;
}
//下面两个for循环检查斜角45度是否有效
i = y - 1;
j = x - 1;
while(i >= 0 && j >= 0) {
if(path[i][j] == 'Q')
return 0;
--i, --j;
}
i = y + 1;
j = x + 1;
while(i < n && j < n) {
if(path[i][j] == 'Q')
return 0;
++i, ++j;
}
//下面两个for循环检查135度是否有效
i = y - 1;
j = x + 1;
while(i >= 0 && j < n) {
if(path[i][j] == 'Q')
return 0;
--i, ++j;
}
i = y + 1;
j = x -1;
while(j >= 0 && i < n) {
if(path[i][j] == 'Q')
return 0;
++i, --j;
}
return 1;
}
void backTracking(int n, int depth) {
//若path中有四个元素,将其拷贝到ans中。从当前层返回
if(pathTop == n) {
copyPath(n);
return;
}
//遍历横向棋盘
int i;
for(i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
//若当前位置有效
if(isValid(i, depth, n)) {
//在当前位置放置皇后
path[depth][i] = 'Q';
//path中元素数量+1
++pathTop;
backTracking(n, depth + 1);
//进行回溯
path[depth][i] = '.';
//path中元素数量-1
--pathTop;
}
}
}
//初始化存储char*数组path,将path中所有元素设为'.'
void initPath(int n) {
int i, j;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++) {
//为path中每个char*开辟空间
path[i] = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * n + 1);
//将path中所有字符设为'.'
for(j = 0; j < n; j++)
path[i][j] = '.';
//在每个字符串结尾加入'\0'
path[i][j] = '\0';
}
}
char *** solveNQueens(int n, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){
//初始化辅助变量
ans = (char***)malloc(sizeof(char**) * 400);
path = (char**)malloc(sizeof(char*) * n);
ansTop = pathTop = 0;
//初始化path数组
initPath(n);
backTracking(n, 0);
//设置返回数组大小
*returnSize = ansTop;
int i;
*returnColumnSizes = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * ansTop);
for(i = 0; i < ansTop; ++i) {
(*returnColumnSizes)[i] = n;
}
return ans;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
# Scala
object Solution {
import scala.collection.mutable
def solveNQueens(n: Int): List[List[String]] = {
var result = mutable.ListBuffer[List[String]]()
def judge(x: Int, y: Int, maze: Array[Array[Boolean]]): Boolean = {
// 正上方
var xx = x
while (xx >= 0) {
if (maze(xx)(y)) return false
xx -= 1
}
// 左边
var yy = y
while (yy >= 0) {
if (maze(x)(yy)) return false
yy -= 1
}
// 左上方
xx = x
yy = y
while (xx >= 0 && yy >= 0) {
if (maze(xx)(yy)) return false
xx -= 1
yy -= 1
}
xx = x
yy = y
// 右上方
while (xx >= 0 && yy < n) {
if (maze(xx)(yy)) return false
xx -= 1
yy += 1
}
true
}
def backtracking(row: Int, maze: Array[Array[Boolean]]): Unit = {
if (row == n) {
// 将结果转换为题目所需要的形式
var path = mutable.ListBuffer[String]()
for (x <- maze) {
var tmp = mutable.ListBuffer[String]()
for (y <- x) {
if (y == true) tmp.append("Q")
else tmp.append(".")
}
path.append(tmp.mkString)
}
result.append(path.toList)
return
}
for (j <- 0 until n) {
// 判断这个位置是否可以放置皇后
if (judge(row, j, maze)) {
maze(row)(j) = true
backtracking(row + 1, maze)
maze(row)(j) = false
}
}
}
backtracking(0, Array.ofDim[Boolean](n, n))
result.toList
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
# C#
public class Solution
{
public List<IList<string>> res = new();
public IList<IList<string>> SolveNQueens(int n)
{
char[][] chessBoard = new char[n][];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
chessBoard[i] = new char[n];
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
chessBoard[i][j] = '.';
}
}
BackTracking(n, 0, chessBoard);
return res;
}
public void BackTracking(int n, int row, char[][] chessBoard)
{
if (row == n)
{
res.Add(chessBoard.Select(x => new string(x)).ToList());
return;
}
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++)
{
if (IsValid(row, col, chessBoard, n))
{
chessBoard[row][col] = 'Q';
BackTracking(n, row + 1, chessBoard);
chessBoard[row][col] = '.';
}
}
}
public bool IsValid(int row, int col, char[][] chessBoard, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
if (chessBoard[i][col] == 'Q') return false;
}
for (int i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--)
{
if (chessBoard[i][j] == 'Q') return false;
}
for (int i = row - 1, j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < n; i--, j++)
{
if (chessBoard[i][j] == 'Q') return false;
}
return true;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
