- 做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目) (opens new window)
- 刷算法(两个月高强度学算法) (opens new window)
- 背八股(40天挑战高频面试题) (opens new window)
双指针风骚起来,也是无敌
# 977.有序数组的平方
给你一个按 非递减顺序 排序的整数数组 nums,返回 每个数字的平方 组成的新数组,要求也按 非递减顺序 排序。
示例 1:
- 输入:nums = [-4,-1,0,3,10]
- 输出:[0,1,9,16,100]
- 解释:平方后,数组变为 [16,1,0,9,100],排序后,数组变为 [0,1,9,16,100]
示例 2:
- 输入:nums = [-7,-3,2,3,11]
- 输出:[4,9,9,49,121]
# 算法公开课
《代码随想录》算法视频公开课 (opens new window):双指针法经典题目!LeetCode:977.有序数组的平方 (opens new window),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解。
# 思路
# 暴力排序
最直观的想法,莫过于:每个数平方之后,排个序,代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> sortedSquares(vector<int>& A) {
for (int i = 0; i < A.size(); i++) {
A[i] *= A[i];
}
sort(A.begin(), A.end()); // 快速排序
return A;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
这个时间复杂度是 O(n + nlogn), 可以说是O(nlogn)的时间复杂度,但为了和下面双指针法算法时间复杂度有鲜明对比,我记为 O(n + nlog n)。
# 双指针法
数组其实是有序的, 只不过负数平方之后可能成为最大数了。
那么数组平方的最大值就在数组的两端,不是最左边就是最右边,不可能是中间。
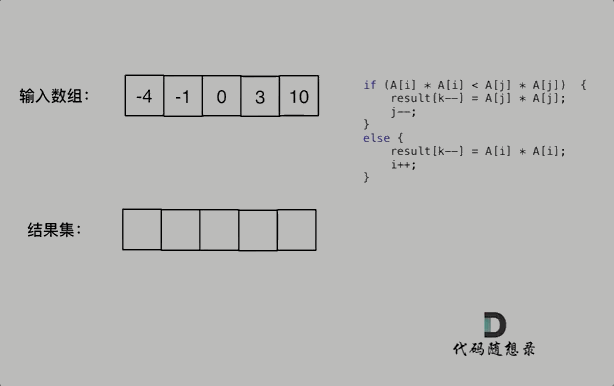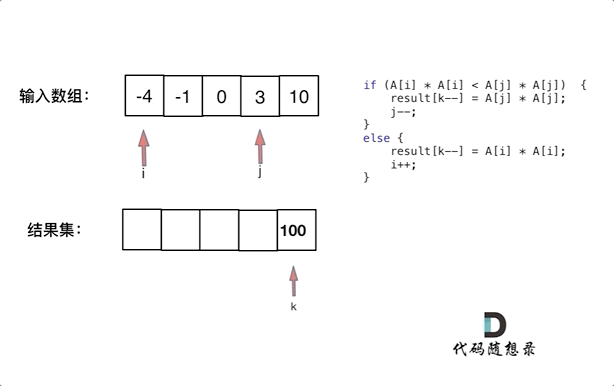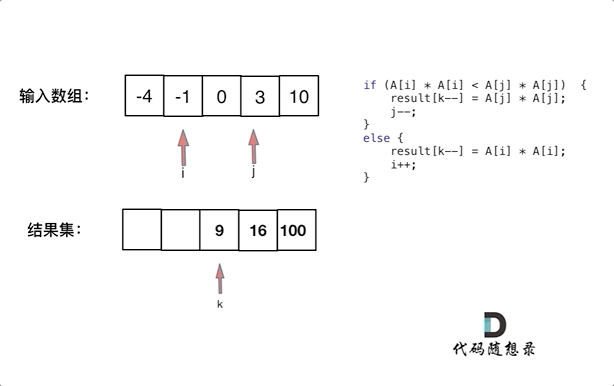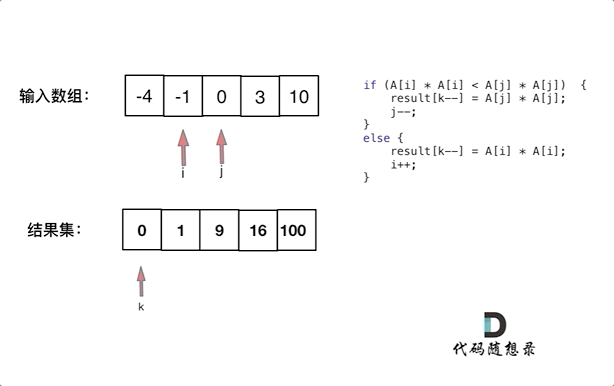
此时可以考虑双指针法了,i指向起始位置,j指向终止位置。
定义一个新数组result,和A数组一样的大小,让k指向result数组终止位置。
如果A[i] * A[i] < A[j] * A[j] 那么result[k--] = A[j] * A[j]; 。
如果A[i] * A[i] >= A[j] * A[j] 那么result[k--] = A[i] * A[i]; 。
如动画所示:
不难写出如下代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> sortedSquares(vector<int>& A) {
int k = A.size() - 1;
vector<int> result(A.size(), 0);
for (int i = 0, j = A.size() - 1; i <= j;) { // 注意这里要i <= j,因为最后要处理两个元素
if (A[i] * A[i] < A[j] * A[j]) {
result[k--] = A[j] * A[j];
j--;
}
else {
result[k--] = A[i] * A[i];
i++;
}
}
return result;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
此时的时间复杂度为O(n),相对于暴力排序的解法O(n + nlog n)还是提升不少的。
这里还是说一下,大家不必太在意leetcode上执行用时,打败多少多少用户,这个就是一个玩具,非常不准确。
做题的时候自己能分析出来时间复杂度就可以了,至于leetcode上执行用时,大概看一下就行,只要达到最优的时间复杂度就可以了,
一样的代码多提交几次可能就击败百分之百了.....
# 其他语言版本
# Java:
排序法
class Solution {
public int[] sortedSquares(int[] nums) {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
nums[i] = nums[i] * nums[i];
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
return nums;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
class Solution {
public int[] sortedSquares(int[] nums) {
int right = nums.length - 1;
int left = 0;
int[] result = new int[nums.length];
int index = result.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
if (nums[left] * nums[left] > nums[right] * nums[right]) {
// 正数的相对位置是不变的, 需要调整的是负数平方后的相对位置
result[index--] = nums[left] * nums[left];
++left;
} else {
result[index--] = nums[right] * nums[right];
--right;
}
}
return result;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
class Solution {
public int[] sortedSquares(int[] nums) {
int l = 0;
int r = nums.length - 1;
int[] res = new int[nums.length];
int j = nums.length - 1;
while(l <= r){
if(nums[l] * nums[l] > nums[r] * nums[r]){
res[j--] = nums[l] * nums[l++];
}else{
res[j--] = nums[r] * nums[r--];
}
}
return res;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# Python:
(版本一)双指针法
class Solution:
def sortedSquares(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
l, r, i = 0, len(nums)-1, len(nums)-1
res = [float('inf')] * len(nums) # 需要提前定义列表,存放结果
while l <= r:
if nums[l] ** 2 < nums[r] ** 2: # 左右边界进行对比,找出最大值
res[i] = nums[r] ** 2
r -= 1 # 右指针往左移动
else:
res[i] = nums[l] ** 2
l += 1 # 左指针往右移动
i -= 1 # 存放结果的指针需要往前平移一位
return res
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
(版本二)暴力排序法
class Solution:
def sortedSquares(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
for i in range(len(nums)):
nums[i] *= nums[i]
nums.sort()
return nums
2
3
4
5
6
7
(版本三)暴力排序法+列表推导法
class Solution:
def sortedSquares(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
return sorted(x*x for x in nums)
2
3
4
(版本四) 双指针+ 反转列表
class Solution:
def sortedSquares(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
#根据list的先进排序在先原则
#将nums的平方按从大到小的顺序添加进新的list
#最后反转list
new_list = []
left, right = 0 , len(nums) -1
while left <= right:
if abs(nums[left]) <= abs(nums[right]):
new_list.append(nums[right] ** 2)
right -= 1
else:
new_list.append(nums[left] ** 2)
left += 1
return new_list[::-1]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
(双指针优化版本) 三步优化
class Solution:
def sortedSquares(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
"""
整体思想:有序数组的绝对值最大值永远在两头,比较两头,平方大的插到新数组的最后
优 化:1. 优化所有元素为非正或非负的情况
2. 头尾平方的大小比较直接将头尾相加与0进行比较即可
3. 新的平方排序数组的插入索引可以用倒序插入实现(针对for循环,while循环不适用)
"""
# 特殊情况, 元素都非负(优化1)
if nums[0] >= 0:
return [num ** 2 for num in nums] # 按顺序平方即可
# 最后一个非正,全负有序的
if nums[-1] <= 0:
return [x ** 2 for x in nums[::-1]] # 倒序平方后的数组
# 一般情况, 有正有负
i = 0 # 原数组头索引
j = len(nums) - 1 # 原数组尾部索引
new_nums = [0] * len(nums) # 新建一个等长数组用于保存排序后的结果
# end_index = len(nums) - 1 # 新的排序数组(是新数组)尾插索引, 每次需要减一(优化3优化了)
for end_index in range(len(nums)-1, -1, -1): # (优化3,倒序,不用单独创建变量)
# if nums[i] ** 2 >= nums[j] ** 2:
if nums[i] + nums[j] <= 0: # (优化2)
new_nums[end_index] = nums[i] ** 2
i += 1
# end_index -= 1 (优化3)
else:
new_nums[end_index] = nums[j] ** 2
j -= 1
# end_index -= 1 (优化3)
return new_nums
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
# Go:
// 排序法
func sortedSquares(nums []int) []int {
for i, val := range nums {
nums[i] *= val
}
sort.Ints(nums)
return nums
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// 双指针法
func sortedSquares(nums []int) []int {
n := len(nums)
i, j, k := 0, n-1, n-1
ans := make([]int, n)
for i <= j {
lm, rm := nums[i]*nums[i], nums[j]*nums[j]
if lm > rm {
ans[k] = lm
i++
} else {
ans[k] = rm
j--
}
k--
}
return ans
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# Rust:
impl Solution {
pub fn sorted_squares(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {
let n = nums.len();
let (mut i,mut j,mut k) = (0,n - 1,n);
let mut ans = vec![0;n];
while i <= j{
if nums[i] * nums[i] < nums[j] * nums[j] {
ans[k-1] = nums[j] * nums[j];
j -= 1;
}else{
ans[k-1] = nums[i] * nums[i];
i += 1;
}
k -= 1;
}
ans
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# JavaScript:
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number[]}
*/
var sortedSquares = function(nums) {
let n = nums.length;
let res = new Array(n).fill(0);
let i = 0, j = n - 1, k = n - 1;
while (i <= j) {
let left = nums[i] * nums[i],
right = nums[j] * nums[j];
if (left < right) {
res[k--] = right;
j--;
} else {
res[k--] = left;
i++;
}
}
return res;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# TypeScript:
双指针法:
function sortedSquares(nums: number[]): number[] {
const ans: number[] = [];
let left = 0,
right = nums.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
// 右侧的元素不需要取绝对值,nums 为非递减排序的整数数组
// 在同为负数的情况下,左侧的平方值一定大于右侧的平方值
if (Math.abs(nums[left]) > nums[right]) {
// 使用 Array.prototype.unshift() 直接在数组的首项插入当前最大值
ans.unshift(nums[left] ** 2);
left++;
} else {
ans.unshift(nums[right] ** 2);
right--;
}
}
return ans;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
骚操作法(暴力思路):
function sortedSquares(nums: number[]): number[] {
return nums.map(i => i * i).sort((a, b) => a - b);
};
2
3
# Swift:
func sortedSquares(_ nums: [Int]) -> [Int] {
// 指向新数组最后一个元素
var k = nums.count - 1
// 指向原数组第一个元素
var i = 0
// 指向原数组最后一个元素
var j = nums.count - 1
// 初始化新数组(用-1填充)
var result = Array<Int>(repeating: -1, count: nums.count)
for _ in 0..<nums.count {
if nums[i] * nums[i] < nums[j] * nums[j] {
result[k] = nums[j] * nums[j]
j -= 1
} else {
result[k] = nums[i] * nums[i]
i += 1
}
k -= 1
}
return result
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# Ruby:
def sorted_squares(nums)
left, right, result = 0, nums.size - 1, []
while left <= right
if nums[left]**2 > nums[right]**2
result << nums[left]**2
left += 1
else
result << nums[right]**2
right -= 1
end
end
result.reverse
end
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# C:
int* sortedSquares(int* nums, int numsSize, int* returnSize){
//返回的数组大小就是原数组大小
*returnSize = numsSize;
//创建两个指针,right指向数组最后一位元素,left指向数组第一位元素
int right = numsSize - 1;
int left = 0;
//最后要返回的结果数组
int* ans = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * numsSize);
int index;
for(index = numsSize - 1; index >= 0; index--) {
//左指针指向元素的平方
int lSquare = nums[left] * nums[left];
//右指针指向元素的平方
int rSquare = nums[right] * nums[right];
//若左指针指向元素平方比右指针指向元素平方大,将左指针指向元素平方放入结果数组。左指针右移一位
if(lSquare > rSquare) {
ans[index] = lSquare;
left++;
}
//若右指针指向元素平方比左指针指向元素平方大,将右指针指向元素平方放入结果数组。右指针左移一位
else {
ans[index] = rSquare;
right--;
}
}
//返回结果数组
return ans;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
# PHP:
class Solution {
/**
* @param Integer[] $nums
* @return Integer[]
*/
function sortedSquares($nums) {
// 双指针法
$res = [];
for ($i = 0; $i < count($nums); $i++) {
$res[$i] = 0;
}
$k = count($nums) - 1;
for ($i = 0, $j = count($nums) - 1; $i <= $j; ) {
if ($nums[$i] ** 2 < $nums[$j] ** 2) {
$res[$k--] = $nums[$j] ** 2;
$j--;
}
else {
$res[$k--] = $nums[$i] ** 2;
$i++;
}
}
return $res;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# Kotlin:
双指针法
class Solution {
// 双指针法
fun sortedSquares(nums: IntArray): IntArray {
var res = IntArray(nums.size)
var left = 0 // 指向数组的最左端
var right = nums.size - 1 // 指向数组端最右端
// 选择平方数更大的那一个往 res 数组中倒序填充
for (index in nums.size - 1 downTo 0) {
if (nums[left] * nums[left] > nums[right] * nums[right]) {
res[index] = nums[left] * nums[left]
left++
} else {
res[index] = nums[right] * nums[right]
right--
}
}
return res
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
骚操作(暴力思路)
class Solution {
fun sortedSquares(nums: IntArray): IntArray {
// left 与 right 用来控制循环,类似于滑动窗口
var left: Int = 0;
var right: Int = nums.size - 1;
// 将每个数字的平方经过排序后加入result数值
var result: IntArray = IntArray(nums.size);
var k: Int = nums.size - 1;
while (left <= right) {
// 从大到小,从后向前填满数组
// [left, right] 控制循环
if (nums[left] * nums[left] > nums[right] * nums[right]) {
result[k--] = nums[left] * nums[left]
left++
}
else {
result[k--] = nums[right] * nums[right]
right--
}
}
return result
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# Scala:
双指针:
object Solution {
def sortedSquares(nums: Array[Int]): Array[Int] = {
val res: Array[Int] = new Array[Int](nums.length)
var top = nums.length - 1
var i = 0
var j = nums.length - 1
while (i <= j) {
if (nums(i) * nums(i) <= nums(j) * nums(j)) {
// 当左侧平方小于等于右侧,res数组顶部放右侧的平方,并且top下移,j左移
res(top) = nums(j) * nums(j)
top -= 1
j -= 1
} else {
// 当左侧平方大于右侧,res数组顶部放左侧的平方,并且top下移,i右移
res(top) = nums(i) * nums(i)
top -= 1
i += 1
}
}
res
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
骚操作(暴力思路):
object Solution {
def sortedSquares(nums: Array[Int]): Array[Int] = {
nums.map(x=>{x*x}).sortWith(_ < _)
}
}
2
3
4
5
# C#:
public class Solution {
public int[] SortedSquares(int[] nums) {
int k = nums.Length - 1;
int[] result = new int[nums.Length];
for (int i = 0, j = nums.Length - 1;i <= j;){
if (nums[i] * nums[i] < nums[j] * nums[j]) {
result[k--] = nums[j] * nums[j];
j--;
} else {
result[k--] = nums[i] * nums[i];
i++;
}
}
return result;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
C# LINQ:
public class Solution {
public int[] SortedSquares(int[] nums) {
return nums.Select(x => x * x).OrderBy(x => x).ToArray();
}
}
2
3
4
5
← 3. 移除元素 5. 长度最小的子数组 →

评论
验证登录状态...