- 做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目) (opens new window)
- 刷算法(两个月高强度学算法) (opens new window)
- 背八股(40天挑战高频面试题) (opens new window)
# 968.监控二叉树
给定一个二叉树,我们在树的节点上安装摄像头。
节点上的每个摄影头都可以监视其父对象、自身及其直接子对象。
计算监控树的所有节点所需的最小摄像头数量。
示例 1:

- 输入:[0,0,null,0,0]
- 输出:1
- 解释:如图所示,一台摄像头足以监控所有节点。
示例 2:
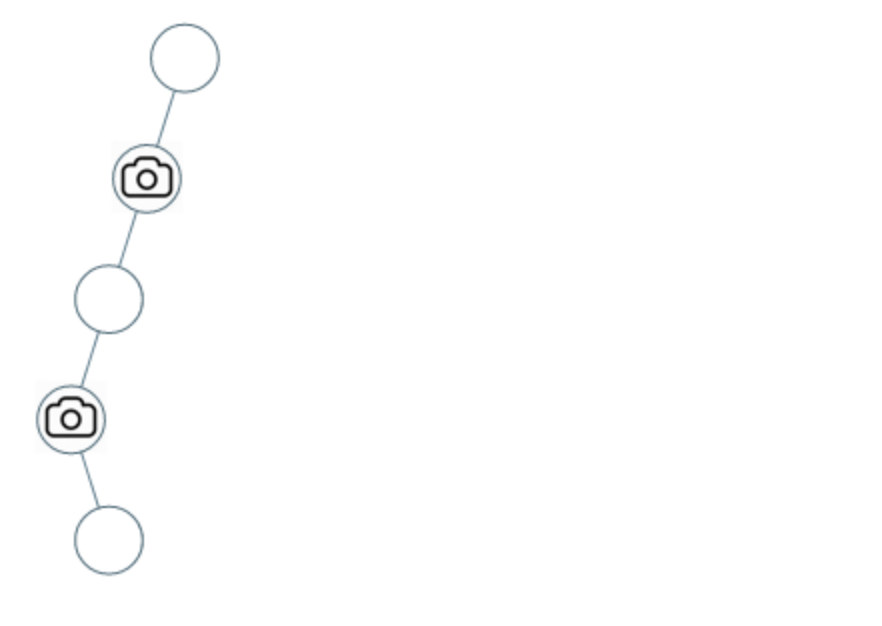
- 输入:[0,0,null,0,null,0,null,null,0]
- 输出:2
- 解释:需要至少两个摄像头来监视树的所有节点。 上图显示了摄像头放置的有效位置之一。
提示:
- 给定树的节点数的范围是 [1, 1000]。
- 每个节点的值都是 0。
# 算法公开课
《代码随想录》算法视频公开课 (opens new window):贪心算法,二叉树与贪心的结合,有点难...... LeetCode:968.监督二叉树 (opens new window),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解。
# 思路
这道题目首先要想,如何放置,才能让摄像头最小的呢?
从题目中示例,其实可以得到启发,我们发现题目示例中的摄像头都没有放在叶子节点上!
这是很重要的一个线索,摄像头可以覆盖上中下三层,如果把摄像头放在叶子节点上,就浪费的一层的覆盖。
所以把摄像头放在叶子节点的父节点位置,才能充分利用摄像头的覆盖面积。
那么有同学可能问了,为什么不从头结点开始看起呢,为啥要从叶子节点看呢?
因为头结点放不放摄像头也就省下一个摄像头, 叶子节点放不放摄像头省下了的摄像头数量是指数阶别的。
所以我们要从下往上看,局部最优:让叶子节点的父节点安摄像头,所用摄像头最少,整体最优:全部摄像头数量所用最少!
局部最优推出全局最优,找不出反例,那么就按照贪心来!
此时,大体思路就是从低到上,先给叶子节点父节点放个摄像头,然后隔两个节点放一个摄像头,直至到二叉树头结点。
此时这道题目还有两个难点:
- 二叉树的遍历
- 如何隔两个节点放一个摄像头
# 确定遍历顺序
在二叉树中如何从低向上推导呢?
可以使用后序遍历也就是左右中的顺序,这样就可以在回溯的过程中从下到上进行推导了。
后序遍历代码如下:
int traversal(TreeNode* cur) {
// 空节点,该节点有覆盖
if (终止条件) return ;
int left = traversal(cur->left); // 左
int right = traversal(cur->right); // 右
逻辑处理 // 中
return ;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
注意在以上代码中我们取了左孩子的返回值,右孩子的返回值,即left 和 right, 以后推导中间节点的状态
# 如何隔两个节点放一个摄像头
此时需要状态转移的公式,大家不要和动态的状态转移公式混到一起,本题状态转移没有择优的过程,就是单纯的状态转移!
来看看这个状态应该如何转移,先来看看每个节点可能有几种状态:
有如下三种:
- 该节点无覆盖
- 本节点有摄像头
- 本节点有覆盖
我们分别有三个数字来表示:
- 0:该节点无覆盖
- 1:本节点有摄像头
- 2:本节点有覆盖
大家应该找不出第四个节点的状态了。
一些同学可能会想有没有第四种状态:本节点无摄像头,其实无摄像头就是 无覆盖 或者 有覆盖的状态,所以一共还是三个状态。
因为在遍历树的过程中,就会遇到空节点,那么问题来了,空节点究竟是哪一种状态呢? 空节点表示无覆盖? 表示有摄像头?还是有覆盖呢?
回归本质,为了让摄像头数量最少,我们要尽量让叶子节点的父节点安装摄像头,这样才能摄像头的数量最少。
那么空节点不能是无覆盖的状态,这样叶子节点就要放摄像头了,空节点也不能是有摄像头的状态,这样叶子节点的父节点就没有必要放摄像头了,而是可以把摄像头放在叶子节点的爷爷节点上。
所以空节点的状态只能是有覆盖,这样就可以在叶子节点的父节点放摄像头了
接下来就是递推关系。
那么递归的终止条件应该是遇到了空节点,此时应该返回2(有覆盖),原因上面已经解释过了。
代码如下:
// 空节点,该节点有覆盖
if (cur == NULL) return 2;
2
递归的函数,以及终止条件已经确定了,再来看单层逻辑处理。
主要有如下四类情况:
- 情况1:左右节点都有覆盖
左孩子有覆盖,右孩子有覆盖,那么此时中间节点应该就是无覆盖的状态了。
如图:
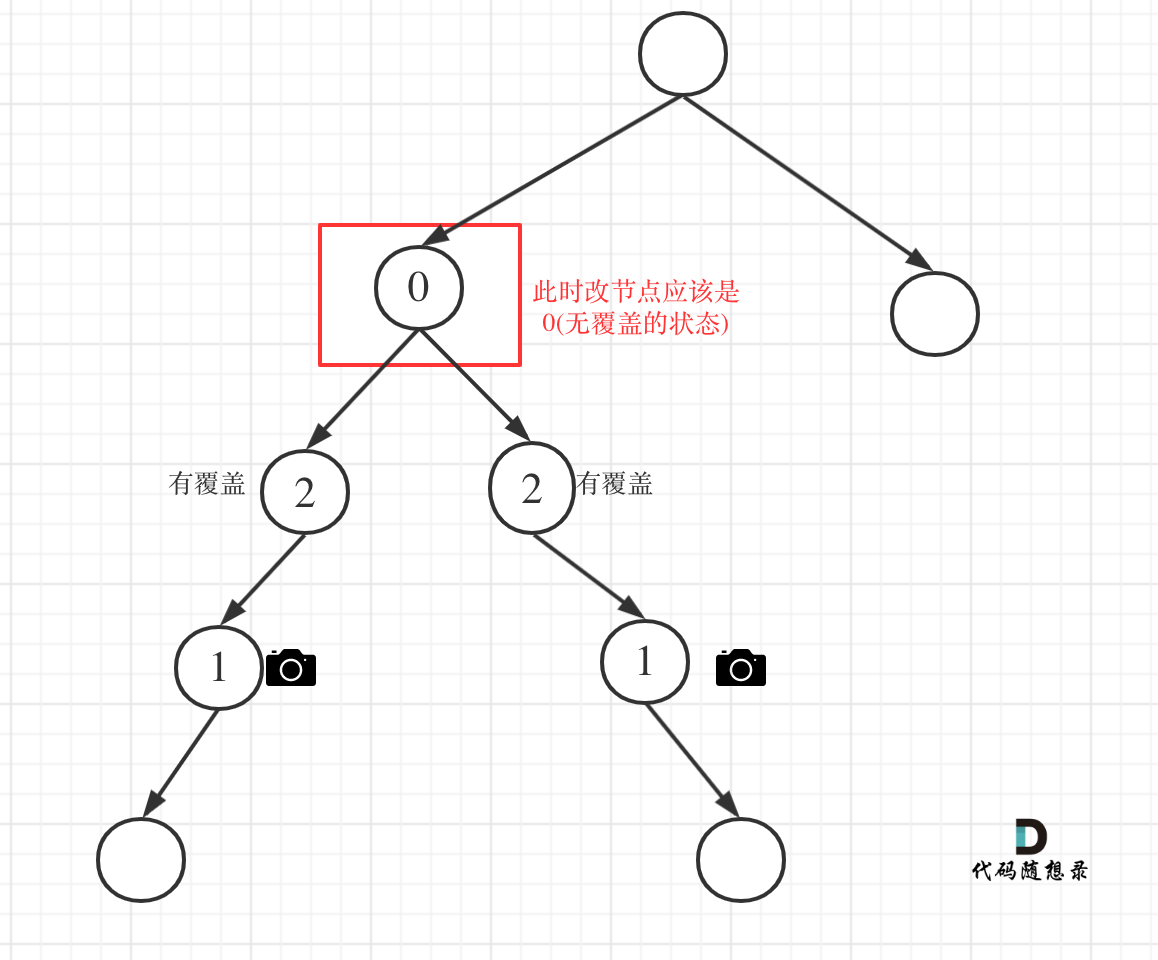
代码如下:
// 左右节点都有覆盖
if (left == 2 && right == 2) return 0;
2
- 情况2:左右节点至少有一个无覆盖的情况
如果是以下情况,则中间节点(父节点)应该放摄像头:
- left == 0 && right == 0 左右节点无覆盖
- left == 1 && right == 0 左节点有摄像头,右节点无覆盖
- left == 0 && right == 1 左节点有无覆盖,右节点摄像头
- left == 0 && right == 2 左节点无覆盖,右节点覆盖
- left == 2 && right == 0 左节点覆盖,右节点无覆盖
这个不难理解,毕竟有一个孩子没有覆盖,父节点就应该放摄像头。
此时摄像头的数量要加一,并且return 1,代表中间节点放摄像头。
代码如下:
if (left == 0 || right == 0) {
result++;
return 1;
}
2
3
4
- 情况3:左右节点至少有一个有摄像头
如果是以下情况,其实就是 左右孩子节点有一个有摄像头了,那么其父节点就应该是2(覆盖的状态)
- left == 1 && right == 2 左节点有摄像头,右节点有覆盖
- left == 2 && right == 1 左节点有覆盖,右节点有摄像头
- left == 1 && right == 1 左右节点都有摄像头
代码如下:
if (left == 1 || right == 1) return 2;
从这个代码中,可以看出,如果left == 1, right == 0 怎么办?其实这种条件在情况2中已经判断过了,如图:
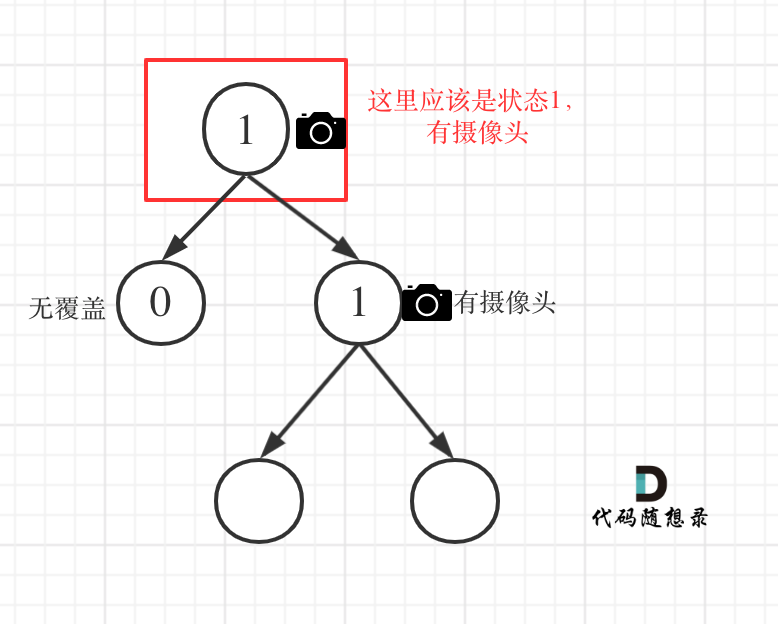
这种情况也是大多数同学容易迷惑的情况。
- 情况4:头结点没有覆盖
以上都处理完了,递归结束之后,可能头结点 还有一个无覆盖的情况,如图:
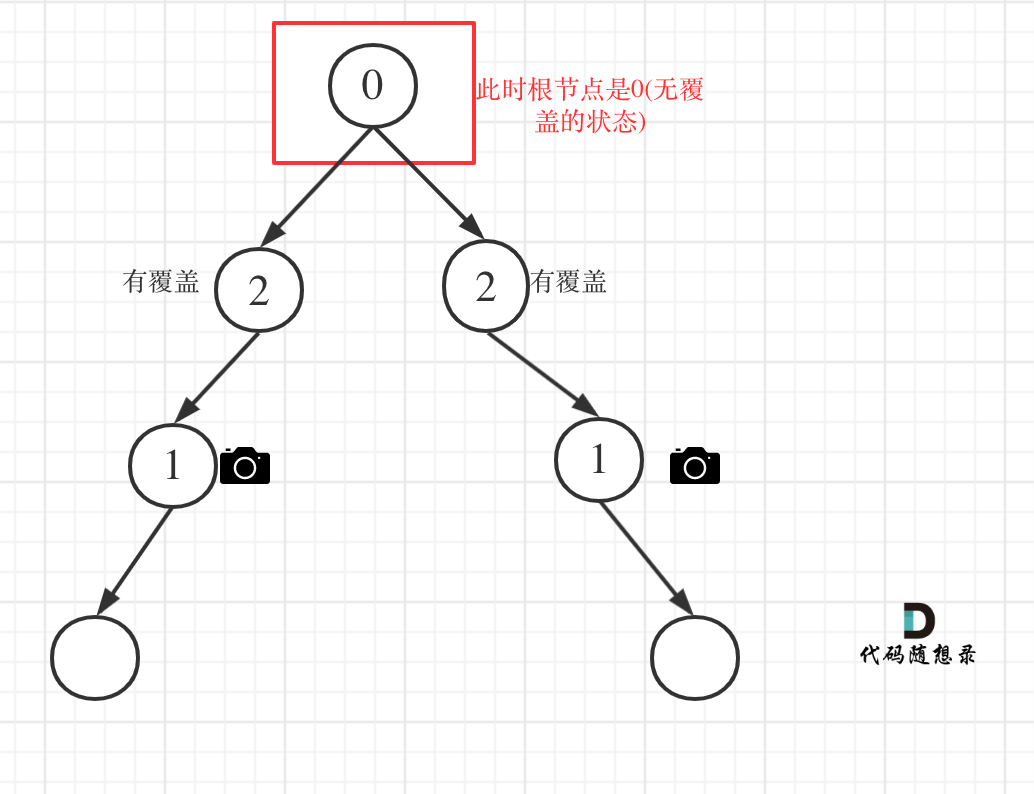
所以递归结束之后,还要判断根节点,如果没有覆盖,result++,代码如下:
int minCameraCover(TreeNode* root) {
result = 0;
if (traversal(root) == 0) { // root 无覆盖
result++;
}
return result;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
以上四种情况我们分析完了,代码也差不多了,整体代码如下:
(以下我的代码注释很详细,为了把情况说清楚,特别把每种情况列出来。)
C++代码如下:
// 版本一
class Solution {
private:
int result;
int traversal(TreeNode* cur) {
// 空节点,该节点有覆盖
if (cur == NULL) return 2;
int left = traversal(cur->left); // 左
int right = traversal(cur->right); // 右
// 情况1
// 左右节点都有覆盖
if (left == 2 && right == 2) return 0;
// 情况2
// left == 0 && right == 0 左右节点无覆盖
// left == 1 && right == 0 左节点有摄像头,右节点无覆盖
// left == 0 && right == 1 左节点有无覆盖,右节点摄像头
// left == 0 && right == 2 左节点无覆盖,右节点覆盖
// left == 2 && right == 0 左节点覆盖,右节点无覆盖
if (left == 0 || right == 0) {
result++;
return 1;
}
// 情况3
// left == 1 && right == 2 左节点有摄像头,右节点有覆盖
// left == 2 && right == 1 左节点有覆盖,右节点有摄像头
// left == 1 && right == 1 左右节点都有摄像头
// 其他情况前段代码均已覆盖
if (left == 1 || right == 1) return 2;
// 以上代码我没有使用else,主要是为了把各个分支条件展现出来,这样代码有助于读者理解
// 这个 return -1 逻辑不会走到这里。
return -1;
}
public:
int minCameraCover(TreeNode* root) {
result = 0;
// 情况4
if (traversal(root) == 0) { // root 无覆盖
result++;
}
return result;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
在以上代码的基础上,再进行精简,代码如下:
// 版本二
class Solution {
private:
int result;
int traversal(TreeNode* cur) {
if (cur == NULL) return 2;
int left = traversal(cur->left); // 左
int right = traversal(cur->right); // 右
if (left == 2 && right == 2) return 0;
else if (left == 0 || right == 0) {
result++;
return 1;
} else return 2;
}
public:
int minCameraCover(TreeNode* root) {
result = 0;
if (traversal(root) == 0) { // root 无覆盖
result++;
}
return result;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
- 时间复杂度: O(n),需要遍历二叉树上的每个节点
- 空间复杂度: O(n)
大家可能会惊讶,居然可以这么简短,其实就是在版本一的基础上,使用else把一些情况直接覆盖掉了。
在网上关于这道题解可以搜到很多这种神级别的代码,但都没讲不清楚,如果直接看代码的话,指定越看越晕,所以建议大家对着版本一的代码一步一步来,版本二中看不中用!。
# 总结
本题的难点首先是要想到贪心的思路,然后就是遍历和状态推导。
在二叉树上进行状态推导,其实难度就上了一个台阶了,需要对二叉树的操作非常娴熟。
这道题目是名副其实的hard,大家感受感受。
# 其他语言版本
# Java
class Solution {
int res=0;
public int minCameraCover(TreeNode root) {
// 对根节点的状态做检验,防止根节点是无覆盖状态 .
if(minCame(root)==0){
res++;
}
return res;
}
/**
节点的状态值:
0 表示无覆盖
1 表示 有摄像头
2 表示有覆盖
后序遍历,根据左右节点的情况,来判读 自己的状态
*/
public int minCame(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
// 空节点默认为 有覆盖状态,避免在叶子节点上放摄像头
return 2;
}
int left=minCame(root.left);
int right=minCame(root.right);
// 如果左右节点都覆盖了的话, 那么本节点的状态就应该是无覆盖,没有摄像头
if(left==2&&right==2){
//(2,2)
return 0;
}else if(left==0||right==0){
// 左右节点都是无覆盖状态,那 根节点此时应该放一个摄像头
// (0,0) (0,1) (0,2) (1,0) (2,0)
// 状态值为 1 摄像头数 ++;
res++;
return 1;
}else{
// 左右节点的 状态为 (1,1) (1,2) (2,1) 也就是左右节点至少存在 1个摄像头,
// 那么本节点就是处于被覆盖状态
return 2;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
简化分支版本:
class Solution {
static int ans;
public int minCameraCover(TreeNode root) {
ans = 0; // 初始化
if(f(root) == 0) ans ++;
return ans;
}
// 定义 f 函数有三种返回值情况
// 0:表示 x 节点没有被相机监控,只能依靠父节点放相机
// 1:表示 x 节点被相机监控,但相机不是放在自身节点上
// 2:表示 x 节点被相机监控,但相机放在自身节点上
public static int f(TreeNode x) {
if(x == null) return 1; // 空树认为被监控,但没有相机
// 左右递归到最深处
int l = f(x.left);
int r = f(x.right);
// 有任意一个子节点为空,就需要当前节点放相机,不然以后没机会
if(l == 0 || r == 0) {
ans ++; // 放相机
return 2;
}
// 贪心策略,左右子树都被监控,且没有监控到当前节点,
// 那么最有利的情况就是将相机放置在当前节点父节点上,
// 因为这样能多监控可能的子树节点和父父节点
if(l == 1 && r == 1) return 0;
// 剩下情况就是左右子树有可能为 2,即当前节点被监控
return 1;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
# Python
贪心(版本一)
class Solution:
# Greedy Algo:
# 从下往上安装摄像头:跳过leaves这样安装数量最少,局部最优 -> 全局最优
# 先给leaves的父节点安装,然后每隔两层节点安装一个摄像头,直到Head
# 0: 该节点未覆盖
# 1: 该节点有摄像头
# 2: 该节点有覆盖
def minCameraCover(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
# 定义递归函数
result = [0] # 用于记录摄像头的安装数量
if self.traversal(root, result) == 0:
result[0] += 1
return result[0]
def traversal(self, cur: TreeNode, result: List[int]) -> int:
if not cur:
return 2
left = self.traversal(cur.left, result)
right = self.traversal(cur.right, result)
# 情况1: 左右节点都有覆盖
if left == 2 and right == 2:
return 0
# 情况2:
# left == 0 && right == 0 左右节点无覆盖
# left == 1 && right == 0 左节点有摄像头,右节点无覆盖
# left == 0 && right == 1 左节点无覆盖,右节点有摄像头
# left == 0 && right == 2 左节点无覆盖,右节点覆盖
# left == 2 && right == 0 左节点覆盖,右节点无覆盖
if left == 0 or right == 0:
result[0] += 1
return 1
# 情况3:
# left == 1 && right == 2 左节点有摄像头,右节点有覆盖
# left == 2 && right == 1 左节点有覆盖,右节点有摄像头
# left == 1 && right == 1 左右节点都有摄像头
if left == 1 or right == 1:
return 2
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
贪心(版本二)利用elif精简代码
class Solution:
# Greedy Algo:
# 从下往上安装摄像头:跳过leaves这样安装数量最少,局部最优 -> 全局最优
# 先给leaves的父节点安装,然后每隔两层节点安装一个摄像头,直到Head
# 0: 该节点未覆盖
# 1: 该节点有摄像头
# 2: 该节点有覆盖
def minCameraCover(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
# 定义递归函数
result = [0] # 用于记录摄像头的安装数量
if self.traversal(root, result) == 0:
result[0] += 1
return result[0]
def traversal(self, cur: TreeNode, result: List[int]) -> int:
if not cur:
return 2
left = self.traversal(cur.left, result)
right = self.traversal(cur.right, result)
# 情况1: 左右节点都有覆盖
if left == 2 and right == 2:
return 0
# 情况2:
# left == 0 && right == 0 左右节点无覆盖
# left == 1 && right == 0 左节点有摄像头,右节点无覆盖
# left == 0 && right == 1 左节点无覆盖,右节点有摄像头
# left == 0 && right == 2 左节点无覆盖,右节点覆盖
# left == 2 && right == 0 左节点覆盖,右节点无覆盖
elif left == 0 or right == 0:
result[0] += 1
return 1
# 情况3:
# left == 1 && right == 2 左节点有摄像头,右节点有覆盖
# left == 2 && right == 1 左节点有覆盖,右节点有摄像头
# left == 1 && right == 1 左右节点都有摄像头
else:
return 2
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
# Go
const inf = math.MaxInt64 / 2
func minCameraCover(root *TreeNode) int {
var dfs func(*TreeNode) (a, b, c int)
dfs = func(node *TreeNode) (a, b, c int) {
if node == nil {
return inf, 0, 0
}
lefta, leftb, leftc := dfs(node.Left)
righta, rightb, rightc := dfs(node.Right)
a = leftc + rightc + 1
b = min(a, min(lefta+rightb, righta+leftb))
c = min(a, leftb+rightb)
return
}
_, ans, _ := dfs(root)
return ans
}
func min(a, b int) int {
if a <= b {
return a
}
return b
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
# JavaScript
var minCameraCover = function(root) {
let result = 0
function traversal(cur) {
if(cur === null) {
return 2
}
let left = traversal(cur.left)
let right = traversal(cur.right)
if(left === 2 && right === 2) {
return 0
}
if(left === 0 || right === 0) {
result++
return 1
}
if(left === 1 || right === 1) {
return 2
}
return -1
}
if(traversal(root) === 0) {
result++
}
return result
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
# TypeScript
function minCameraCover(root: TreeNode | null): number {
/** 0-无覆盖, 1-有摄像头, 2-有覆盖 */
type statusCode = 0 | 1 | 2;
let resCount: number = 0;
if (recur(root) === 0) resCount++;
return resCount;
function recur(node: TreeNode | null): statusCode {
if (node === null) return 2;
const left: statusCode = recur(node.left),
right: statusCode = recur(node.right);
let resStatus: statusCode = 0;
if (left === 0 || right === 0) {
resStatus = 1;
resCount++;
} else if (left === 1 || right === 1) {
resStatus = 2;
} else {
resStatus = 0;
}
return resStatus;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# C
/*
**函数后序遍历二叉树。判断一个结点状态时,根据其左右孩子结点的状态进行判断
**状态:0为没有被摄像头覆盖到。1为此结点处应设置摄像头。2为此结点已被摄像头覆盖
*/
int traversal(struct TreeNode* node, int* ans) {
//递归结束条件:传入结点为NULL,假设此结点能被摄像头覆盖。这样方便与对叶子结点的判断,将叶子结点设为0
if(!node)
return 2;
//后序遍历二叉树,记录左右孩子的状态。根据左右孩子状态更新结点自身状态
int left = traversal(node->left, ans);
int right = traversal(node->right, ans);
//若左右孩子都可以被摄像头覆盖,将父亲结点状态设为0
if(left == 2 && right == 2) {
return 0;
}
//若左右孩子有一个结点状态为没有被覆盖(0),则将父亲结点状态设置为摄像头
if(left == 0 || right == 0) {
(*ans)++;
return 1;
}
//若左右孩子有一个为摄像头,证明父亲结点可以被覆盖。将父亲结点状态变为2
if(left == 1 || right == 1)
return 2;
//逻辑不会走到-1,语句不会执行
return -1;
}
int minCameraCover(struct TreeNode* root){
int ans = 0;
//在对整个二叉树遍历后。头结点可能未被覆盖,这时候如果函数返回值为0,证明头结点未被覆盖。说明头结点也需要添置摄像头,ans++
if(traversal(root, &ans) == 0)
ans++;
return ans;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
# Scala
object Solution {
def minCameraCover(root: TreeNode): Int = {
var result = 0
def traversal(cur: TreeNode): Int = {
// 空节点,该节点有覆盖
if (cur == null) return 2
var left = traversal(cur.left)
var right = traversal(cur.right)
// 情况1,左右节点都有覆盖
if (left == 2 && right == 2) {
return 0
}
// 情况2
if (left == 0 || right == 0) {
result += 1
return 1
}
// 情况3
if (left == 1 || right == 1) {
return 2
}
-1
}
if (traversal(root) == 0) {
result += 1
}
result
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
# Rust
/// 版本一
impl Solution {
pub fn min_camera_cover(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 {
let mut res = 0;
if Self::traversal(&root, &mut res) == 0 {
res += 1;
}
res
}
pub fn traversal(cur: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, ans: &mut i32) -> i32 {
// 0 未覆盖 1 节点已设置摄像头 2 节点已覆盖
if let Some(node) = cur {
let node = node.borrow();
let left = Self::traversal(&node.left, ans);
let right = Self::traversal(&node.right, ans);
// 左右节点都被覆盖
if left == 2 && right == 2 {
return 0; // 无覆盖
}
// left == 0 right == 0 左右无覆盖
// left == 0 right == 1 左节点无覆盖 右节点有摄像头
// left == 1 right == 0 左节点有摄像头 左节点无覆盖
// left == 0 right == 2 左节点无覆盖 右节点有覆盖
// left == 2 right == 0 左节点有覆盖 右节点无覆盖
if left == 0 || right == 0 {
*ans += 1;
return 1;
}
// left == 1 right == 1 左节点有摄像头 右节点有摄像头
// left == 1 right == 2 左节点有摄像头 右节点覆盖
// left == 2 right == 1 左节点覆盖 右节点有摄像头
if left == 1 || right == 1 {
return 2; // 已覆盖
}
} else {
return 2;
}
-1
}
}
/// 版本二
enum NodeState {
NoCover = 0,
Camera = 1,
Covered = 2,
}
impl Solution {
pub fn min_camera_cover(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 {
let mut res = 0;
let state = Self::traversal(&root, &mut res);
match state {
NodeState::NoCover => res + 1,
_ => res,
}
}
pub fn traversal(cur: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, ans: &mut i32) -> NodeState {
if let Some(node) = cur {
let node = node.borrow();
let left_state = Self::traversal(&node.left, ans);
let right_state = Self::traversal(&node.right, ans);
match (left_state, right_state) {
(NodeState::NoCover, _) | (_, NodeState::NoCover) => {
*ans += 1;
NodeState::Camera
}
(NodeState::Camera, _) | (_, NodeState::Camera) => NodeState::Covered,
(_, _) => NodeState::NoCover,
}
} else {
NodeState::Covered
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
# C#
public class Solution
{
public int res = 0;
public int MinCameraCover(TreeNode root)
{
if (Traversal(root) == 0) res++;
return res;
}
public int Traversal(TreeNode cur)
{
if (cur == null) return 2;
int left = Traversal(cur.left);
int right = Traversal(cur.right);
if (left == 2 && right == 2) return 0;
else if (left == 0 || right == 0)
{
res++;
return 1;
}
else return 2;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
