- 做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目) (opens new window)
- 刷算法(两个月高强度学算法) (opens new window)
- 背八股(40天挑战高频面试题) (opens new window)
利用二叉搜索树的特性搞起!
# 530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
给你一棵所有节点为非负值的二叉搜索树,请你计算树中任意两节点的差的绝对值的最小值。
示例:

提示:树中至少有 2 个节点。
# 算法公开课
《代码随想录》算法视频公开课 (opens new window):二叉搜索树中,需要掌握如何双指针遍历!| LeetCode:530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差 (opens new window),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解。
# 思路
题目中要求在二叉搜索树上任意两节点的差的绝对值的最小值。
注意是二叉搜索树,二叉搜索树可是有序的。
遇到在二叉搜索树上求什么最值啊,差值之类的,就把它想成在一个有序数组上求最值,求差值,这样就简单多了。
# 递归
那么二叉搜索树采用中序遍历,其实就是一个有序数组。
在一个有序数组上求两个数最小差值,这是不是就是一道送分题了。
最直观的想法,就是把二叉搜索树转换成有序数组,然后遍历一遍数组,就统计出来最小差值了。
代码如下:
class Solution {
private:
vector<int> vec;
void traversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return;
traversal(root->left);
vec.push_back(root->val); // 将二叉搜索树转换为有序数组
traversal(root->right);
}
public:
int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode* root) {
vec.clear();
traversal(root);
if (vec.size() < 2) return 0;
int result = INT_MAX;
for (int i = 1; i < vec.size(); i++) { // 统计有序数组的最小差值
result = min(result, vec[i] - vec[i-1]);
}
return result;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
以上代码是把二叉搜索树转化为有序数组了,其实在二叉搜素树中序遍历的过程中,我们就可以直接计算了。
需要用一个pre节点记录一下cur节点的前一个节点。
如图:
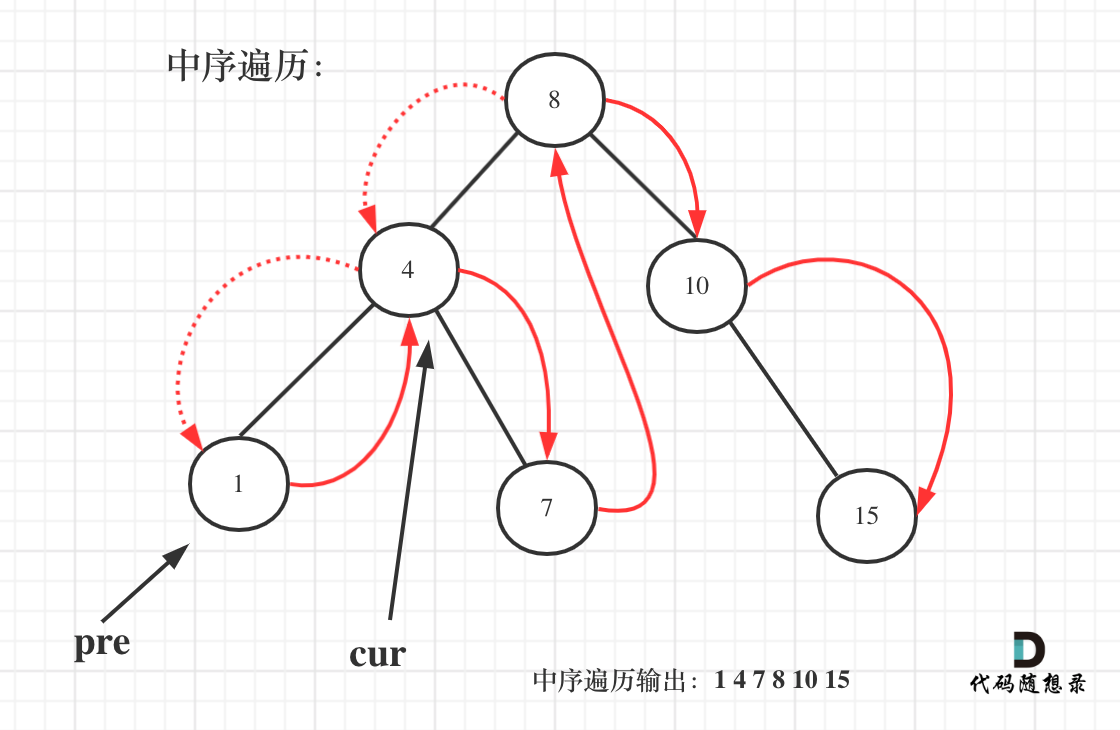
一些同学不知道在递归中如何记录前一个节点的指针,其实实现起来是很简单的,大家只要看过一次,写过一次,就掌握了。
代码如下:
class Solution {
private:
int result = INT_MAX;
TreeNode* pre = NULL;
void traversal(TreeNode* cur) {
if (cur == NULL) return;
traversal(cur->left); // 左
if (pre != NULL){ // 中
result = min(result, cur->val - pre->val);
}
pre = cur; // 记录前一个
traversal(cur->right); // 右
}
public:
int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode* root) {
traversal(root);
return result;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
是不是看上去也并不复杂!
# 迭代
看过这两篇二叉树:听说递归能做的,栈也能做! (opens new window),二叉树:前中后序迭代方式的写法就不能统一一下么? (opens new window)文章之后,不难写出两种中序遍历的迭代法。
下面我给出其中的一种中序遍历的迭代法,代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode* cur = root;
TreeNode* pre = NULL;
int result = INT_MAX;
while (cur != NULL || !st.empty()) {
if (cur != NULL) { // 指针来访问节点,访问到最底层
st.push(cur); // 将访问的节点放进栈
cur = cur->left; // 左
} else {
cur = st.top();
st.pop();
if (pre != NULL) { // 中
result = min(result, cur->val - pre->val);
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur->right; // 右
}
}
return result;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# 总结
遇到在二叉搜索树上求什么最值,求差值之类的,都要思考一下二叉搜索树可是有序的,要利用好这一特点。
同时要学会在递归遍历的过程中如何记录前后两个指针,这也是一个小技巧,学会了还是很受用的。
后面我将继续介绍一系列利用二叉搜索树特性的题目。
# 其他语言版本
# Java
递归
class Solution {
TreeNode pre; // 记录上一个遍历的结点
int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
traversal(root);
return result;
}
public void traversal(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return;
// 左
traversal(root.left);
// 中
if (pre != null) {
result = Math.min(result, root.val - pre.val);
}
pre = root;
// 右
traversal(root.right);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
統一迭代法-中序遍历
class Solution {
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode pre = null;
int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if (root != null)
stack.add(root);
// 中序遍历(左中右),由于栈先入后出,反序(右中左)
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode curr = stack.peek();
if (curr != null) {
stack.pop();
// 右
if (curr.right != null)
stack.add(curr.right);
// 中(先用null标记)
stack.add(curr);
stack.add(null);
// 左
if (curr.left != null)
stack.add(curr.left);
} else { // 中(遇到null再处理)
stack.pop();
TreeNode temp = stack.pop();
if (pre != null)
result = Math.min(result, temp.val - pre.val);
pre = temp;
}
}
return result;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
迭代法-中序遍历
class Solution {
TreeNode pre;
Stack<TreeNode> stack;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur); // 将访问的节点放进栈
cur = cur.left; // 左
}else {
cur = stack.pop();
if (pre != null) { // 中
result = Math.min(result, cur.val - pre.val);
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur.right; // 右
}
}
return result;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# Python
递归法(版本一)利用中序递增,结合数组
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.vec = []
def traversal(self, root):
if root is None:
return
self.traversal(root.left)
self.vec.append(root.val) # 将二叉搜索树转换为有序数组
self.traversal(root.right)
def getMinimumDifference(self, root):
self.vec = []
self.traversal(root)
if len(self.vec) < 2:
return 0
result = float('inf')
for i in range(1, len(self.vec)):
# 统计有序数组的最小差值
result = min(result, self.vec[i] - self.vec[i - 1])
return result
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
递归法(版本二)利用中序递增,找到该树最小值
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.result = float('inf')
self.pre = None
def traversal(self, cur):
if cur is None:
return
self.traversal(cur.left) # 左
if self.pre is not None: # 中
self.result = min(self.result, cur.val - self.pre.val)
self.pre = cur # 记录前一个
self.traversal(cur.right) # 右
def getMinimumDifference(self, root):
self.traversal(root)
return self.result
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
迭代法
class Solution:
def getMinimumDifference(self, root):
stack = []
cur = root
pre = None
result = float('inf')
while cur is not None or len(stack) > 0:
if cur is not None:
stack.append(cur) # 将访问的节点放进栈
cur = cur.left # 左
else:
cur = stack.pop()
if pre is not None: # 中
result = min(result, cur.val - pre.val)
pre = cur
cur = cur.right # 右
return result
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# Go
中序遍历,然后计算最小差值
// 中序遍历的同时计算最小值
func getMinimumDifference(root *TreeNode) int {
// 保留前一个节点的指针
var prev *TreeNode
// 定义一个比较大的值
min := math.MaxInt64
var travel func(node *TreeNode)
travel = func(node *TreeNode) {
if node == nil {
return
}
travel(node.Left)
if prev != nil && node.Val - prev.Val < min {
min = node.Val - prev.Val
}
prev = node
travel(node.Right)
}
travel(root)
return min
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# JavaScript
递归 先转换为有序数组
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var getMinimumDifference = function (root) {
let arr = [];
const buildArr = (root) => {
if (root) {
buildArr(root.left);
arr.push(root.val);
buildArr(root.right);
}
}
buildArr(root);
let diff = arr[arr.length - 1];
for (let i = 1; i < arr.length; ++i) {
if (diff > arr[i] - arr[i - 1])
diff = arr[i] - arr[i - 1];
}
return diff;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
递归 在递归的过程中更新最小值
var getMinimumDifference = function(root) {
let res = Infinity
let preNode = null
// 中序遍历
const inorder = (node) => {
if(!node) return
inorder(node.left)
// 更新res
if(preNode) res = Math.min(res, node.val - preNode.val)
// 记录前一个节点
preNode = node
inorder(node.right)
}
inorder(root)
return res
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
迭代 中序遍历
var getMinimumDifference = function(root) {
let stack = []
let cur = root
let res = Infinity
let pre = null
while(cur || stack.length) {
if(cur) {
stack.push(cur)
cur = cur.left
} else {
cur = stack.pop()
if(pre) res = Math.min(res, cur.val - pre.val)
pre = cur
cur = cur.right
}
}
return res
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# TypeScript
辅助数组解决
function getMinimumDifference(root: TreeNode | null): number {
let helperArr: number[] = [];
function recur(root: TreeNode | null): void {
if (root === null) return;
recur(root.left);
helperArr.push(root.val);
recur(root.right);
}
recur(root);
let resMin: number = Infinity;
for (let i = 0, length = helperArr.length; i < length - 1; i++) {
resMin = Math.min(resMin, helperArr[i + 1] - helperArr[i]);
}
return resMin;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
递归中解决
function getMinimumDifference(root: TreeNode | null): number {
let preNode: TreeNode | null= null;
let resMin: number = Infinity;
function recur(root: TreeNode | null): void {
if (root === null) return;
recur(root.left);
if (preNode !== null) {
resMin = Math.min(resMin, root.val - preNode.val);
}
preNode = root;
recur(root.right);
}
recur(root);
return resMin;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
迭代法-中序遍历
function getMinimumDifference(root: TreeNode | null): number {
const helperStack: TreeNode[] = [];
let curNode: TreeNode | null = root;
let resMin: number = Infinity;
let preNode: TreeNode | null = null;
while (curNode !== null || helperStack.length > 0) {
if (curNode !== null) {
helperStack.push(curNode);
curNode = curNode.left;
} else {
curNode = helperStack.pop()!;
if (preNode !== null) {
resMin = Math.min(resMin, curNode.val - preNode.val);
}
preNode = curNode;
curNode = curNode.right;
}
}
return resMin;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# Scala
构建二叉树的有序数组:
object Solution {
import scala.collection.mutable
def getMinimumDifference(root: TreeNode): Int = {
val arr = mutable.ArrayBuffer[Int]()
def traversal(node: TreeNode): Unit = {
if (node == null) return
traversal(node.left)
arr.append(node.value)
traversal(node.right)
}
traversal(root)
// 在有序数组上求最小差值
var result = Int.MaxValue
for (i <- 1 until arr.size) {
result = math.min(result, arr(i) - arr(i - 1))
}
result // 返回最小差值
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
递归记录前一个节点:
object Solution {
def getMinimumDifference(root: TreeNode): Int = {
var result = Int.MaxValue // 初始化为最大值
var pre: TreeNode = null // 记录前一个节点
def traversal(cur: TreeNode): Unit = {
if (cur == null) return
traversal(cur.left)
if (pre != null) {
// 对比result与节点之间的差值
result = math.min(result, cur.value - pre.value)
}
pre = cur
traversal(cur.right)
}
traversal(root)
result // return关键字可以省略
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
迭代解决:
object Solution {
import scala.collection.mutable
def getMinimumDifference(root: TreeNode): Int = {
var result = Int.MaxValue // 初始化为最大值
var pre: TreeNode = null // 记录前一个节点
var cur = root
var stack = mutable.Stack[TreeNode]()
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty) {
if (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur)
cur = cur.left
} else {
cur = stack.pop()
if (pre != null) {
result = math.min(result, cur.value - pre.value)
}
pre = cur
cur = cur.right
}
}
result // return关键字可以省略
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# Rust
构建二叉树的有序数组:
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::rc::Rc;
impl Solution {
pub fn get_minimum_difference(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 {
let mut vec = vec![];
Self::traversal(root, &mut vec);
let mut min = i32::MAX;
for i in 1..vec.len() {
min = min.min(vec[i] - vec[i - 1])
}
min
}
pub fn traversal(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, v: &mut Vec<i32>) {
if root.is_none() {
return;
}
let node = root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow();
Self::traversal(node.left.clone(), v);
v.push(node.val);
Self::traversal(node.right.clone(), v);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
递归中解决
impl Solution {
pub fn get_minimum_difference(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 {
let mut pre = None;
let mut min = i32::MAX;
Self::inorder(root, &mut pre, &mut min);
min
}
pub fn inorder(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, pre: &mut Option<i32>, min: &mut i32) {
if root.is_none() {
return;
}
let node = root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow();
Self::inorder(node.left.clone(), pre, min);
if let Some(pre) = pre {
*min = (node.val - *pre).min(*min);
}
*pre = Some(node.val);
Self::inorder(node.right.clone(), pre, min);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
迭代
impl Solution {
pub fn get_minimum_difference(mut root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 {
if root.is_none() {
return 0;
}
let mut stack = vec![];
let mut pre = -1;
let mut res = i32::MAX;
while root.is_some() || !stack.is_empty() {
while let Some(node) = root {
root = node.borrow().left.clone();
stack.push(node);
}
let node = stack.pop().unwrap();
if pre >= 0 {
res = res.min(node.borrow().val - pre);
}
pre = node.borrow().val;
root = node.borrow().right.clone();
}
res
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
# C#
// 递归
public class Solution
{
public List<int> res = new List<int>();
public int GetMinimumDifference(TreeNode root)
{
Traversal(root);
return res.SelectMany((x, i) => res.Skip(i + 1).Select(y => Math.Abs(x - y))).Min();
}
public void Traversal(TreeNode root)
{
if (root == null) return;
Traversal(root.left);
res.Add(root.val);
Traversal(root.right);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
