- 做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目) (opens new window)
- 刷算法(两个月高强度学算法) (opens new window)
- 背八股(40天挑战高频面试题) (opens new window)
# 1356. 根据数字二进制下 1 的数目排序
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/sort-integers-by-the-number-of-1-bits/
给你一个整数数组 arr 。请你将数组中的元素按照其二进制表示中数字 1 的数目升序排序。
如果存在多个数字二进制中 1 的数目相同,则必须将它们按照数值大小升序排列。
请你返回排序后的数组。
示例 1:
- 输入:arr = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]
- 输出:[0,1,2,4,8,3,5,6,7]
- 解释:[0] 是唯一一个有 0 个 1 的数。 [1,2,4,8] 都有 1 个 1 。 [3,5,6] 有 2 个 1 。 [7] 有 3 个 1 。按照 1 的个数排序得到的结果数组为 [0,1,2,4,8,3,5,6,7]
示例 2:
- 输入:arr = [1024,512,256,128,64,32,16,8,4,2,1]
- 输出:[1,2,4,8,16,32,64,128,256,512,1024]
- 解释:数组中所有整数二进制下都只有 1 个 1 ,所以你需要按照数值大小将它们排序。
示例 3:
- 输入:arr = [10000,10000]
- 输出:[10000,10000]
示例 4:
- 输入:arr = [2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19]
- 输出:[2,3,5,17,7,11,13,19]
示例 5:
- 输入:arr = [10,100,1000,10000]
- 输出:[10,100,10000,1000]
# 思路
这道题其实是考察如何计算一个数的二进制中1的数量。
我提供两种方法:
- 方法一:
朴实无华挨个计算1的数量,最多就是循环n的二进制位数,32位。
int bitCount(int n) {
int count = 0; // 计数器
while (n > 0) {
if((n & 1) == 1) count++; // 当前位是1,count++
n >>= 1 ; // n向右移位
}
return count;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
- 方法二
这种方法,只循环n的二进制中1的个数次,比方法一高效的多
int bitCount(int n) {
int count = 0;
while (n) {
n &= (n - 1); // 清除最低位的1
count++;
}
return count;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
以计算12的二进制1的数量为例,如图所示:
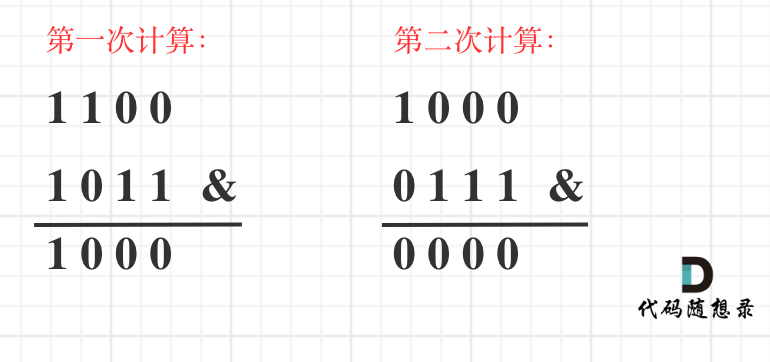
下面我就使用方法二,来做这道题目:
class Solution {
private:
static int bitCount(int n) { // 计算n的二进制中1的数量
int count = 0;
while(n) {
n &= (n -1); // 清除最低位的1
count++;
}
return count;
}
static bool cmp(int a, int b) {
int bitA = bitCount(a);
int bitB = bitCount(b);
if (bitA == bitB) return a < b; // 如果bit中1数量相同,比较数值大小
return bitA < bitB; // 否则比较bit中1数量大小
}
public:
vector<int> sortByBits(vector<int>& arr) {
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end(), cmp);
return arr;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# 其他语言版本
# Java
class Solution {
private int cntInt(int val){
int count = 0;
while(val > 0) {
val = val & (val - 1);
count ++;
}
return count;
}
public int[] sortByBits(int[] arr) {
return Arrays.stream(arr).boxed()
.sorted(new Comparator<Integer>(){
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
int cnt1 = cntInt(o1);
int cnt2 = cntInt(o2);
return (cnt1 == cnt2) ? Integer.compare(o1, o2) : Integer.compare(cnt1, cnt2);
}
})
.mapToInt(Integer::intValue)
.toArray();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# Python
class Solution:
def sortByBits(self, arr: List[int]) -> List[int]:
arr.sort(key=lambda num: (self.count_bits(num), num))
return arr
def count_bits(self, num: int) -> int:
count = 0
while num:
num &= num - 1
count += 1
return count
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# Go
func sortByBits(arr []int) []int {
// 是否arr[i]<=arr[j]
// 先比较1的数量,后比较值本身
cmp := func(i, j int) bool {
c1, c2 := bitCount(arr[i]), bitCount(arr[j])
if c1 == c2 {
return arr[i] <= arr[j]
}
return c1 <= c2
}
// 调用库函数
// 第一个参数是待排序切片,第二个是第i位是否小于第j位的函数
sort.Slice(arr, cmp)
return arr
}
func bitCount(num int) (count int) {
for num != 0 {
num &= num-1 // 每次运算将最右侧的1变成0
count++
}
return count
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
# JavaScript
var sortByBits = function(arr) {
const bitCount = n =>{// 计算n的二进制中1的数量
let count = 0;
while(n){
n &= (n - 1);// 清除最低位的1
count++;
}
return count;
}
// 如果有差,则按bits数排,如果无差,则按原值排
return arr.sort((a,b) => bitCount(a) - bitCount(b) || a - b);
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
@2021-2026 代码随想录 版权所有 粤ICP备19156078号
